neck-pain
This systematic review and meta-analysis investigated the effectiveness and safety of manual therapy (MT) interventions compared to oral or topical pain medications in the management of neck pain.
The investigators searched from inception to March 2023, in Cochrane Central Register of Controller Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, EMBASE, Allied and Complementary Medicine (AMED) and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL; EBSCO) for randomized controlled trials that examined the effect of manual therapy interventions for neck pain when compared to oral or topical medication in adults with self-reported neck pain, irrespective of radicular findings, specific cause, and associated cervicogenic headaches. Trials with usual care arms were also included if they prescribed medication as part of the usual care and they did not include a manual therapy component. The authors used the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool to assess the potential risk of bias in the included studies, and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations (GRADE) approach to grade the quality of the evidence.
Nine trials with a total of 779 participants were included in the meta-analysis.
- low certainty of evidence was found that MT interventions may be more effective than oral pain medication in pain reduction in the short-term (Standardized Mean Difference: -0.39; 95% CI -0.66 to -0.11; 8 trials, 676 participants),
- moderate certainty of evidence was found that MT interventions may be more effective than oral pain medication in pain reduction in the long-term (Standardized Mean Difference: −0.36; 95% CI −0.55 to −0.17; 6 trials, 567 participants),
- low certainty evidence that the risk of adverse events may be lower for patients who received MT compared to the ones that received oral pain medication (Risk Ratio: 0.59; 95% CI 0.43 to 0.79; 5 trials, 426 participants).
The authors conluded that MT may be more effective for people with neck pain in both short and long-term with a better safety profile regarding adverse events when compared to patients receiving oral pain medications. However, we advise caution when interpreting our safety results due to the different level of reporting strategies in place for MT and medication-induced adverse events. Future MT trials should create and adhere to strict reporting strategies with regards to adverse events to help gain a better understanding on the nature of potential MT-induced adverse events and to ensure patient safety.
Let’s have a look at the primary studies. Here they are with their conclusions (and, where appropriate, my comments in capital letters):
- For participants with acute and subacute neck pain, spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) was more effective than medication in both the short and long term. However, a few instructional sessions of home exercise with (HEA) resulted in similar outcomes at most time points. EXERCISE WAS AS EFFECTIVE AS SMT
- Oral ibuprofen (OI) pharmacologic treatment may reduce pain intensity and disability with respect to neural mobilization (MNNM and CLG) in patients with CP during six weeks. Nevertheless, the non-existence of between-groups ROM differences and possible OI adverse effects should be considered. MEDICATION WAS BETTER THAN MT
- It appears that both treatment strategies (usual care + MT vs usual care) can have equivalent positive influences on headache complaints. Additional studies with larger study populations are needed to draw firm conclusions. Recommendations to increase patient inflow in primary care trials, such as the use of an extended network of participating physicians and of clinical alert software applications, are discussed. MT DOES NOT IMPROVE OUTCOMES
- The consistency of the results provides, in spite of several discussed shortcomings of this pilot study, evidence that in patients with chronic spinal pain syndromes spinal manipulation, if not contraindicated, results in greater improvement than acupuncture and medicine. THIS IS A PILOT STUDY, A TRIAL TESTING FEASIBILITY, NOT EFFECTIVENESS
- The consistency of the results provides, despite some discussed shortcomings of this study, evidence that in patients with chronic spinal pain, manipulation, if not contraindicated, results in greater short-term improvement than acupuncture or medication. However, the data do not strongly support the use of only manipulation, only acupuncture, or only nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs for the treatment of chronic spinal pain. The results from this exploratory study need confirmation from future larger studies.
- In daily practice, manual therapy is a favorable treatment option for patients with neck pain compared with physical therapy or continued care by a general practitioner.
- Short-term results (at 7 weeks) have shown that MT speeded recovery compared with GP care and, to a lesser extent, also compared with PT. In the long-term, GP treatment and PT caught up with MT, and differences between the three treatment groups decreased and lost statistical significance at the 13-week and 52-week follow-up. MT IS NOT SUPERIOR [SAME TRIAL AS No 6]
- In this randomized clinical trial, for patients with chronic neck pain, Chuna manual therapy was more effective than usual care in terms of pain and functional recovery at 5 weeks and 1 year after randomization. These results support the need to consider recommending manual therapies as primary care treatments for chronic neck pain.
- In patients with chronic spinal pain syndromes, spinal manipulation, if not contraindicated, may be the only treatment modality of the assessed regimens that provides broad and significant long-term benefit. SAME TRIAL AS No 5
- An impairment-based manual physical therapy and exercise (MTE) program resulted in clinically and statistically significant short- and long-term improvements in pain, disability, and patient-perceived recovery in patients with mechanical neck pain when compared to a program comprising advice, a mobility exercise, and subtherapeutic ultrasound. THIS STUDY DID NOT TEST MT ALONE AND SHOULD NOT HAVE BEEN INCLUDED
I cannot bring myself to characterising this as an overall positive result for MT; anyone who can is guilty of wishful thinking, in my view. The small differences in favor of MT that (some of) the trials report have little to do with the effectiveness of MT itself. They are almost certainly due to the fact that none of these studies were placebo-controlled and double blind (even though this would clearly be possible). In contrast to popping a pill, MT involves extra attention, physical touch, empathy, etc. These factors easily suffice to bring about the small differences that some studies report.
It follows that the main conclusion of the authors of the review should be modified:
There is no compelling evidence to show that MT is more effective for people with neck pain in both short and long-term when compared to patients receiving oral pain medications.
Cervical spondylosis is a chronic degenerative process of the cervical spine characterized by pain in neck, degenerative changes in intervertebral disc and osteophyte formation. The present study was aimed at evaluating the effect of wet cupping (Ḥijāma Bish Sharṭ) in the pain management of cervical spondylosis.
This Open, randomized, clinical study was conducted on 44 patients.
- Subjects in the test group (n = 22) received a series of three-staged wet cupping treatment, performed on 0, 7th and 14th day.
- Subjects in the control group (n = 22) received 12 sittings of Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): 6 sittings per week for two weeks.
The outcomes were assessed with the help of VAS, Neck Disability Index (NDI) and Cervical range of motion.
Intra group comparison in test group from baseline to 21st day were found highly significant (p < 0.001) in terms of VAS, NDI, Flexion, Extension and Left rotation score. While in Right rotation, Left rotation and Left lateral flexion score were found moderately significant (p < 0.01). Statistically significant difference was observed between two groups at 21st day in VAS scale, NDI, and Cervical range of motion score (p < 0.001).
The authors concluded that Ḥijāma Bish Sharṭ was found better in the management of pain due to cervical spondylosis than TENS. It can be concluded that Ḥijāma Bish Sharṭ may a better option for the pain management of cervical spondylosis.
Wet cupping is the use of a vacuum cup applied to the skin which has previously been lacerated. It draws blood and can thus be seen as a form of blood letting. It has been used in various cultures for the treatment of joint pain and many other conditions since antiquity.
The authors point out that, in Unani medicine, it is believed to reduce pain and other symptoms by diverting and evacuating the causative pathological humours (akhlāṭ-e-fasida). Galen (Jalinoos) mentioned wet cupping as a very useful modality in evacuating the thick humours (akhlāṭ-e-Ghaleez) (Nafeesi, 1954; Qamri, 2008). Wet cupping works on the principle of diversion and evacuation of morbid matter (imala wa tanqiya-i-mawād-i-fasida). It opens the pores of the skin, enhances the blood circulation, nourishes the affected area with fresh blood, improves the eliminative function and facilitates the evacuation of morbid matter from the body.
There are several studies of wet cupping, most of which are as flawed as the one above. This new trial has several limitations, e.g.:
- It makes no attempt to control for placebo effects which could well be more prominent for wet cupping than for TENS.
- It did not inhibit the influence of verbal or non-verbal communications between therapists and patients which are likely to influence the results.
- The sample size is far too small, particularly as the study was designed as an equivalence study.
But some might say that my arguments a petty and argue that, regardless of a flimsy study, wet cupping is still worth a try. I would disagree – not because of the flaws of this study, nor the implausibility of the long-obsolete assumptions that underpin the therapy, but because wet cupping is associaated with infections of the skin lacerations which occasionally can be serious.
This study tested whether trigger point acupuncture (TrPA) is beneficial for office workers who have reduced job performance (presenteeism) due to chronic neck and shoulder pain (katakori).
A 4-week single-center randomized clinical trial was conducted on 20 eligible female office workers with chronic neck and shoulder pain of at least 3-month duration. The control group implemented only workplace-recommended presenteeism measures, whereas the intervention group received TrPA up to 4 times per month in addition to the presenteeism measures recommended by each workplace. The major outcome measure was the relative presenteeism score on the World Health Organization Health and Work Performance (WHO-HPQ). The secondary outcome measures were pain intensity (numerical rating scale), absolute presenteeism (WHO-HPQ), anxiety and depression (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; HADS), catastrophic thoughts related to pain (Pain Catastrophizing Scale; PCS), and sleep (Athens Insomnia Scale; AIS).
All 9 cases in the intervention group and 11 cases in the control group were analyzed. TrPA up to 4 times per month reduced the intensity of neck and shoulder pain by 20% (P < .01, d = 1.65) and improved labor productivity (relative presenteeism value) by 0.25 (P < .01, d = 1.33) compared with the control group over 1 month. No significant differences were observed between the 2 groups in terms of absolute presenteeism score, HADS, PCS, or AIS.
The authors concluded that these results suggest that regular intervention with TrPA may be effective in the relative presenteeism score before and after the intervention and the degree of neck and shoulder pain over 28 days compared with the control group.
Sure, TrPA may be effective.
But is it?
I thought the trial was aimed at answering that question!
But it didn’t!
Why not?
Because, as we have discussed ad nauseam on this blog, the A+B versus B study design cannot answer it. On the contrary, it will always generate a positive result without determining whether the treatment or a nonspecific (placebo) effect caused the outcome (which, of course, is the reason why this study design is so popular in SCAM research).
In view of this, I suggest to re-formulate the conclusions as follows:
The study suggests that the researchers were ill-informed when designing it. Therefore, the findings show nothing of value.
The purpose of this systematic review was to assess the effectiveness and safety of conservative interventions compared with other interventions, placebo/sham interventions, or no intervention on disability, pain, function, quality of life, and psychological impact in adults with cervical radiculopathy (CR), a painful condition caused by the compression or irritation of the nerves that supply the shoulders, arms and hands.
A multidisciplinary team autors searched MEDLINE, CENTRAL, CINAHL, Embase, and PsycINFO from inception to June 15, 2022 to identify studies that were:
- randomized trials,
- had at least one conservative treatment arm,
- diagnosed participants with CR through confirmatory clinical examination and/or diagnostic tests.
Studies were appraised using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool and the quality of the evidence was rated using the Grades of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach.
Of the 2561 records identified, 59 trials met the inclusion criteria (n = 4108 participants). Due to clinical and statistical heterogeneity, the findings were synthesized narratively.
There is very-low certainty evidence supporting the use of:
- acupuncture,
- prednisolone,
- cervical manipulation,
- low-level laser therapy
for pain and disability in the immediate to short-term, and
- thoracic manipulation,
- low-level laser therapy
for improvements in cervical range of motion in the immediate term.
There is low to very-low certainty evidence for multimodal interventions, providing inconclusive evidence for pain, disability, and range of motion.
There is inconclusive evidence for pain reduction after conservative management compared with surgery, rated as very-low certainty.
The authors concluded that there is a lack of high-quality evidence, limiting our ability to make any meaningful conclusions. As the number of people with CR is expected to increase, there is an urgent need for future research to help address these gaps.
I agree!
Yet, to patients suffering from CR, this is hardly constructive advice. What should they do vis a vis such disappointing evidence?
They might speak to a orthopedic surgeon; but often there is no indication for an operation. What then?
Patients are bound to try some of the conservative options – but which one?
- Acupuncture?
- Prednisolone?
- Cervical manipulation,?
- Low-level laser therapy?
My advice is this: be patient – the vast majority of cases resolves spontaneously regardless of therapy – and, if you are desperate, try any of them except cervical manipulation which is burdened with the risk of serious complications and often makes things worse.
This systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) estimated the benefits and harms of cervical spinal manipulative therapy (SMT) for treating neck pain. The authors searched the MEDLINE, Cochrane CENTRAL, EMBASE, CINAHL, PEDro, Chiropractic Literature Index bibliographic databases, and grey literature sources, up to June 6, 2022.
RCTs evaluating SMT compared to guideline-recommended and non-recommended interventions, sham SMT, and no intervention for adults with neck pain were eligible. Pre-specified outcomes included pain, range of motion, disability, health-related quality of life.
A total of 28 RCTs could be included. There was very low to low certainty evidence that SMT was more effective than recommended interventions for improving pain at short-term (standardized mean difference [SMD] 0.66; confidence interval [CI] 0.35 to 0.97) and long-term (SMD 0.73; CI 0.31 to 1.16), and for reducing disability at short-term (SMD 0.95; CI 0.48 to 1.42) and long-term (SMD 0.65; CI 0.23 to 1.06). Only transient side effects were found (e.g., muscle soreness).
The authors concluded that there was very low certainty evidence supporting cervical SMT as an intervention to reduce pain and improve disability in people with neck pain.
Harms cannot be adequately investigated on the basis of RCT data. Firstly, because much larger sample sizes would be required for this purpose. Secondly, RCTs of spinal manipulation very often omit reporting adverse effects (as discussed repeatedly on this bolg). If we extend our searches beyond RCTs, we find many cases of serious harm caused by neck manipulations (also as discussed repeatedly on this bolg). Therefore, the conclusion of this review should be corrected:
Low certainty evidence exists supporting cervical SMT as an intervention to reduce pain and improve disability in people with neck pain. The evidence of harm is, however, substantial. It follows that the risk/benefit ratio is not positive. Cervical SMT should therefore be discouraged.
In a video, Mr.Darkmoore speaks from a hospital bed and says the cause behind his visit to the emergency room stemmed from a chiropractor’s work on him. Three days ago, he had a ringing in his ear due to a long-term condition he knew as tinnitus. Thus, he decided to visit a chiropractor. “I figured $100 to a chiro, let them adjust a few things, if all else fails, I’ll go to a doctor,” explains Darkmoore.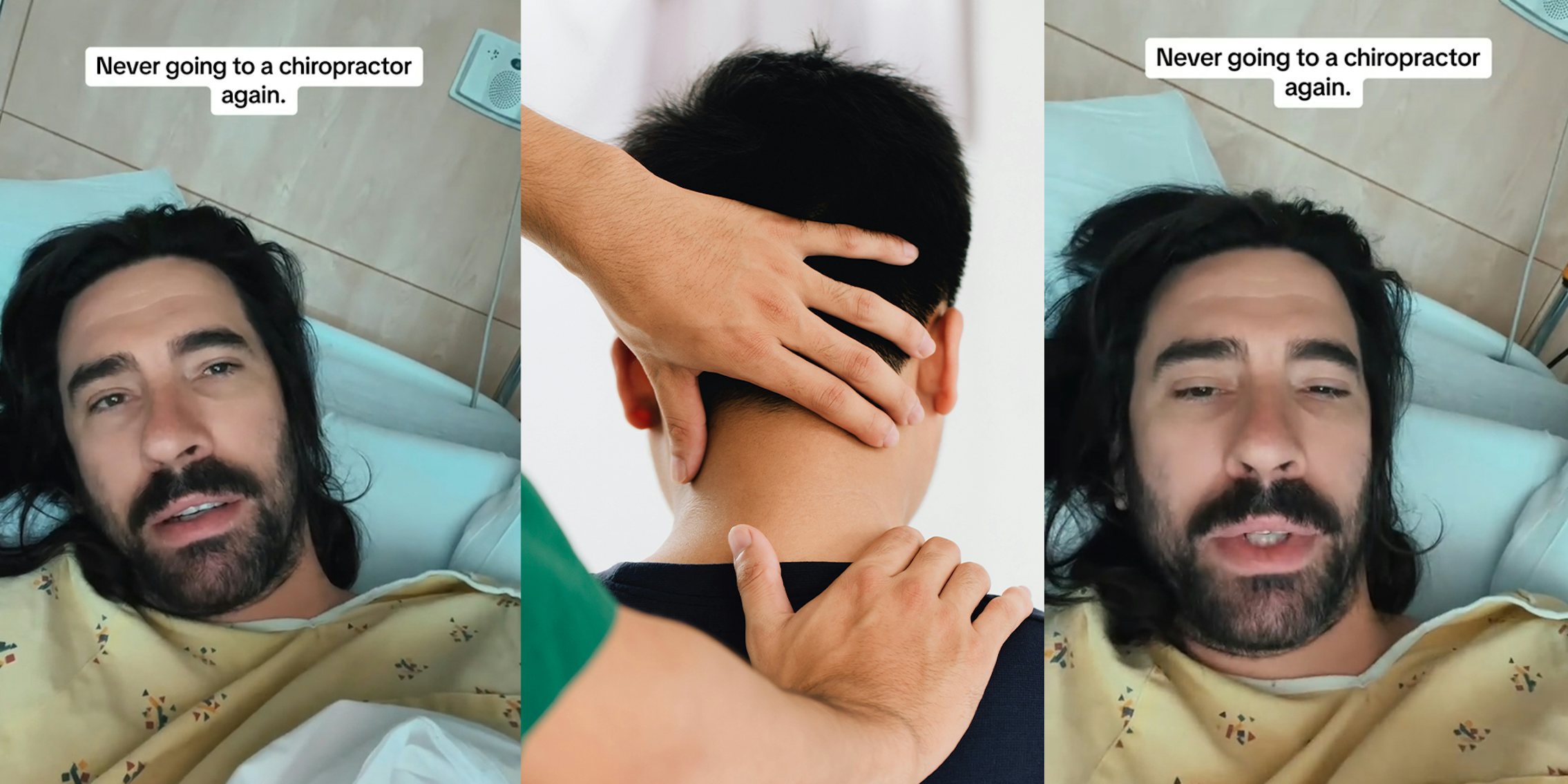
This $100 visit led to several other complications and doctor’s bills worth thousands of dollars. The day after he was treated by the chiropractor, he experienced a headache that eventually led to dizzy spells. He decided to visit the emergency room where a CT scan was ordered which showed that the chiropractor had dissected an artery in his neck.
Next, Darkmoore was put on blood thinners to avoid blood clots that could result in a stroke or worse. Darkmoore explains that he will be on two blood thinners for the next three months to prevent clotting. If the dissection heals partially, he says he will need to take aspirin every day for the rest of his life. If it doesn’t heal, he claims that he will need surgery.
Many viewers of the video claimed they have had the same “chiropractor gone wrong” experience as Darkmoore.
- “Wow. How scary. I had a similar thing happen to me. Extremely bad headache after going one time. Haven’t gone since,” one commenter wrote.
- “I’m so sorry this happened to u,” another user echoed. “My chiropractor also caused an injury which required emergency surgery & I have permanent damage. I’m glad u survived.”
Darkmore captioned his last update video, “I appreciate the thoughts and prayers. Hopefully, I’ll be okay after 3 months of recovery.”
__________________
Let’s hope that he is correct and that he will make a speedy and full recovery.
Of course, chiros will queue up to stress that important details are missing in this case report. To them, I would merely say this:
THERE IS NO GOOD EVIDENCE THAT NECK MANIPULATIONS BRING ANY BENEFIT AND QUITE A BIT OF EVIDENCE THAT THEY CAN CAUSE SERIOUS HARM.
SO, WHY NOT JUST STOP OFFERING THE PROCEDURE?
Cervical spondylosis (CS) is a general term for wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in the neck. As these disks age, they shrink and signs of osteoarthritis can develop, including bony projections along the edges of bones (bone spurs). CS is very common and worsens with age. About 85% of people over 60 are affected by cervical spondylosis. For most of them, it causes no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, non-surgical treatments often are effective. I think there are not many so-called alternative treatments that are not being promoted as effective for CS – often with the support of some lousy clinical trials. Homeopathy does not seem to be an exception.
This trial attempted evaluating the efficacy of individualized homeopathic medicines (IHMs) against placebos in the treatment of CS.
A 3-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted at the Organon of Medicine outpatient department of the National Institute of Homoeopathy, India. Patients were randomized to receive either IHMs (n = 70) or identical-looking placebos (n = 70) in the mutual context of concomitant conservative and standard physiotherapeutic care. Primary outcome measures were 0-10 Numeric Rating Scales (NRSs) for pain, stiffness, numbness, tingling, weakness, and vertigo, and the secondary outcome was the Neck Disability Index (NDI), measured at baseline and every month until 3 months. The intention-to-treat sample was analyzed to detect group differences and effect sizes.
Overall, improvements were clinically significant and higher in the IHM group than in the placebo group, but group differences were statistically nonsignificant with small effect sizes (all p > 0.05, two-way repeated measure analysis of variance). After 2 months of time points, improvements observed in the IHM group were significantly higher than placebo on a few occasions (e.g., pain NRS: p < 0.001; stiffness NRS: p = 0.024; weakness NRS: p = 0.003). Sulfur (n = 21; 15%) was the most frequently prescribed medication. No harm, unintended effects, or any serious adverse events were reported from either group.
The authors concluded that an encouraging but nonsignificant direction of effect was elicited favoring IHMs against placebos in the treatment of CS.
I agree that it is encouraging that Indian homeopaths have recently dared to publish also negative findings! However, I do not agree that the findings are encouraging in the sense that they indicate anything other than that homeopathy is a placebo therapy.
Unfortunately, I cannot access the full article without paying for it. Thus I am unable to provide detailed criticism of this study – sorry.
Cervical radiculopathy is a common condition that is usually due to compression or injury to a nerve root by a herniated disc or other degenerative changes of the upper spine. The C5 to T1 levels are the most commonly affected. In such cases local and radiating pains, often with neurological deficits, are the most prominent symptoms. Treatment of this condition is often difficult.
The purpose of this systematic review was to assess the effectiveness and safety of conservative interventions compared with other interventions, placebo/sham interventions, or no intervention on disability, pain, function, quality of life, and psychological impact in adults with cervical radiculopathy (CR).
MEDLINE, CENTRAL, CINAHL, Embase, and PsycINFO were searched from inception to June 15, 2022, to identify studies that were randomized clinical trials, had at least one conservative treatment arm, and diagnosed participants with CR through confirmatory clinical examination and/or diagnostic tests. Studies were appraised using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 tool and the quality of the evidence was rated using the Grades of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach.
Of the 2561 records identified, 59 trials met our inclusion criteria (n = 4108 participants). Due to clinical and statistical heterogeneity, the findings were synthesized narratively. The results show very-low certainty evidence supporting the use of
- acupuncture,
- prednisolone,
- cervical manipulation,
- low-level laser therapy
for pain and disability in the immediate to short-term, and thoracic manipulation and low-level laser therapy for improvements in cervical range of motion in the immediate term.
There is low to very-low certainty evidence for multimodal interventions, providing inconclusive evidence for pain, disability, and range of motion. There is inconclusive evidence for pain reduction after conservative management compared with surgery, rated as very-low certainty.
The authors concluded that there is a lack of high-quality evidence, limiting our ability to make any meaningful conclusions. As the number of people with CR is expected to increase, there is an urgent need for future research to help address these gaps.
The fact that we cannot offer a truly effective therapy for CR has long been known – except, of course, to chiropractors, acupuncturists, osteopaths, and other SCAM providers who offer their services as though they are a sure solution. Sometimes, their treatments seem to work; but this could be just because the symptoms of CR can improve spontaneously, unrelated to any intervention.
The question thus arises what should these often badly suffering patients do if spontaneous remission does not occur? As an answer, let me quote from another recent systematic review of the subject: The 6 included studies that had low risk of bias, providing high-quality evidence for the surgical efficacy of Cervical Spondylotic Radiculopathy. The evidence indicates that surgical treatment is better than conservative treatment … and superior to conservative treatment in less than one year.
Yes, this post is yet again about the harm chiropractors do.
No, I am not obsessed with the subject – I merely consider it to be important.
This is a case presentation of a 44-year-old male who was transferred from another emergency department for left homonymous inferior quadrantanopia noted on an optometrist visit. He reported sudden onset left homonymous hemianopia after receiving a high-velocity cervical spine adjustment at a chiropractor appointment for chronic neck pain a few days prior.
The CT angiogram of the head and neck revealed bilateral vertebral artery dissection at the left V2 and right V3 segments. MRI brain confirmed an acute infarct in the right medial occipital lobe. His right PCA stroke was likely embolic from the injured right V3 but possibly from the left V2 as well. As the patient reported progression from a homonymous hemianopia to a quadrantanopia, he likely had a migrating embolus.
The authors discussed that arterial dissection accounts for about 2% of all ischemic strokes, but maybe between 8–25% in patients less than 45 years old. Vertebral artery dissection (VAD) can result from trauma from sports, motor vehicle accidents, and chiropractor neck manipulations to violent coughing/sneezing.
It is estimated that 1 in 20,000 spinal manipulation results in vertebral artery aneurysm/dissection. Patients who have multiple chronic conditions are reporting higher use of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM), including chiropractic manipulation. Education about the association between VAD and chiropractor maneuvers can be beneficial to the public as these are preventable acute ischemic strokes. In addition, VAD symptoms can be subtle and patients presenting to chiropractors may have distracting pain masking their deficits. Evaluating for appropriateness of cervical manipulation in high‐risk patients and detecting early clinical signs of VAD by chiropractors can be beneficial in preventing acute ischemic strokes in young patients.
Here we have a rare instance where the physicians who treated the chiro-victim were sufficiently motivated to present their findings and document them in the medical literature. Their report was published in 2021 as an abstract in conference proceedings. In other words, the report is not easy to find. Even though two years have passed, the full article does not seem to have emerged, and chances are that it will never be published.
The points I am trying to make are as follows:
- Complications after chiropractic manipulation do happen and are probably much more frequent than chiros want us to believe.
- They are only rarely reported in the medical literature because the busy clinicians who end up treating the victims do not consider this a priority and because many cases are settled in or out of court.
- Normally, it would be the ethical/moral duty of the chiros who have inflicted the damage to do the reporting.
- Yet, they seem too busy ripping off more patients by doing neck manipulations that do more harm than good.
- And then they complain that the evidence is insufficient!!!
I came across an article that seems highly relevant to our recurring debates about the dangers of chiropractic. Since few of us might be readers of the Louisville Courier, I take the liberty of reproducing here a shortened version of it:
Amber Burgess, then 33, had never set foot in a chiropractor’s office when she went to Dr. Adam Fulkerson’s Heartland Family Chiropractic in Elizabethtown on May 18, 2020. In contrast, Becca Barlow, 31, had seen Dr. Leah Wright at Louisville Family Chiropractic 29 times for adjustments over three years when she went there on Jan. 7, 2019, seeking relief for “nursing mother’s neck.” Both say they will never see a chiropractor again. “That visit was my first – and last,” said Burgess, a former utility bucket-truck assembler.
In separate lawsuits, they claim they suffered strokes after chiropractic adjustments; Barlow, herself a nurse, said she realized she was having one before she even left the office and told Wright’s staff to call 911.
Citing studies on human cadavers and other research, chiropractors claim adjustments are physically incapable of causing tears to arteries that in turn cause strokes by blocking the flow of blood to the brain and other organs. In an opening statement in the trial of Barlow’s suit last March, attorney John Floyd Jr., counsel for Wright and the National Chiropractic Mutual Insurance Co., said no one has ever proved adjustments cause the tears – known as dissection – only that there is an “association” between them. “We associate the crowing of roosters with sunrise,” he told the jury. “But that doesn’t mean roosters cause the sun to come up.” Floyd also cited studies he said prove that when a patient strokes out immediately after adjustments, like Barlow, it is because they already were suffering from artery injuries when they sought treatment from their chiropractor.
Louisville attorney Brian Clare, who represents both Barlow and Burgess, previously settled two cases in Jefferson County, and has another suit pending in Warren Circuit Court. He said in an interview that “every time chiropractors perform adjustments on the neck they are playing with fire. They can go too far, too fast, turning the neck past therapeutic limits,” he said.
The jury in Barlow’s case emphatically rejected the chiropractic profession’s defenses. “We found those claims to be unbelievable,” said jury foreman Joseph Tucker, a lawyer, who noted Barlow had no symptoms before her adjustments. By a 9-3 vote, the jury awarded her $1,130,800, including $380,000 in medical expenses and $750,000 for pain and suffering.
Witnesses testified that Barlow fell off the table and vomited almost immediately after her adjustment, showing classic stroke symptoms, including vertigo, dizziness, numbness, and nausea. She lost consciousness, had to be intubated in an ambulance, then raced to Norton Brownsboro Hospital, where she underwent emergency surgery to restore the flow of blood to her arteries and save her life. Three of the four arteries in her neck had been dissected.
Burgess, in Elizabethtown, suffered a stroke in her spine that her expert, Dr. Louis Caplan, a neurology professor at Harvard University, said also was caused by her cervical manipulations. Caplan says he’s cared for more than 15,000 stroke patients over 45 years.
Fulkerson has denied liability; his lawyer, James Grohman, said he couldn’t comment because the case is pending; the trial is set for Aug. 28 in Hardin Circuit Court Caplan said in a report that Burgess’s stroke left her with partial but permanent paralysis in her arms and legs. She uses a wheelchair and walker with wheels to get around. She said she can’t work, can’t drive, and that while she can dress herself, it takes hours to get ready. She fears they will have to give up their plans to have a baby.
By any measure, strokes associated with adjustments are rare, although their incidence is disputed. The American Chiropractic Association says arteries are damaged in only one to three adjustments out of 100,000 But a 2001 report in the New England Journal of Medicine estimated dissections occur in 1 of 20,000 adjustments. And Dr. Alan Brafman, an Atlanta chiropractor, has said they occur more often than that. Brafman wrote that he’s consulted in 1,100 cases, including Barlow’s, and found in most of them, chiropractors were at fault, causing vascular damage that is “a tragic, life-altering situation for all parties involved.” Wright’s experts themselves divulged they had been retained in 200 cases, according to Clare, which he said suggests chiropractic-related strokes are more common than suspected. A survey at Stanford University in 2008 of 177 neurologists found 55 had patients who suffered strokes after seeing chiropractors, while a 2018 study in West Virginia found one in 48 chiropractors experienced such an event. Neurologists and other physicians point to a 2001 study in STROKE of 582 stroke patients that found they were five times more likely to have seen a chiropractor in the previous five days before their artery dissection than a control group without such injuries. The American Heart Association and other medical groups recommend that patients also be warned about the risks; Barlow said she never would have undergone her final manipulation if she had been informed.
__________________________
Yet again, I am impressed by the number of cases that go to court where a settlement of some sort is reached and further reporting of the incident is prevented. As a consequence, these cases are not published in the medical literature. In turn, this means that chiropractors can continue to claim that these complications do not exist or are exceedingly rare.
- The truth, however, is that NOBODY can provide accurate incidence figures.
- The truth is that, even if such complications were rare, they are devastating.
- The truth is that neck manipulations do not generate any or very little benefit.
- The truth is that their risk/benefit balance is not positive.
- The truth is that we, therefore, have an ethical duty to tell potential patients about it.
I feel that I cannot repeat my warning often enough:
AVOID CHIROPRACTORS.
THEY CAUSE MORE HARM THAN GOOD!
