supplements
Few of us are aware of the fact that there are such things as alternative diagnoses, i.e. diagnoses used by practitioners of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) that have no basis in science. They are nonetheless popular with some SCAM practitioners and usually cause a wide range of non-specific symptoms.
In part 1 of this series of posts, I dealt with:
- adrenal fatigue,
- candidiasis hypersensitivity,
- chronic intoxications.
Today I will briefly discuss three further alternative diagnoses.
Chronic Lyme Disease
Lyme disease exists, of course; it is a bacterial infection attained via the bite of a tick. By contrast chronic lyme disease is pure fantasy. It is often used to explain persistent pain, fatigue, and neurocognitive symptoms in patients without any evidence of previous acute lyme disease.
Once this diagnosis is given, prolonged treatment with multiple antimicrobial agents as well as a multitude of SCAMs are advocated. The range includes intravenous infusions of hydrogen peroxide, electromagnetic frequency treatments, garlic supplements, even stem cell transplants.
Unsurprisingly, none of them has been shown to work for chronic lyme disease.
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS) is a condition where individuals report symptoms attributed to exposure to electromagnetic fields. It is not a recognized medical diagnosis.
Symptoms of EHS include headache, fatigue, stress, sleep disturbances, skin prickling, burning sensations and rashes, pain, psychological distress and many other health problems. The true case seems psychosomatic and unrelated to electromagnetic fields.
Practitioners nevertheless recommend all sorts of SCAMs including chelation, detox, diets, tocopherols , carotenoids, vitamin C, curcumin, resveratrol, flavonoids, sauna, blue light therapy none of which have been shown to be effective.
Homosexuality
Yes, it’s true: some SCAM practitioners offer treatments for homosexuality which must mean that they consider it to be a disease.
As reported in a previous blog post, the German ‘Association of Catholic Doctors’, Bund Katholischer Ärzte, claims that homeopathic remedies can cure homosexuality. On their website, they advise that ‘…the working group HOMEOPATHY of the Association notes homeopathic therapy options for homosexual tendencies…repertories contain special rubrics pointing to characteristic signs of homosexual behaviour, including sexual peculiarities such as anal intercourse.
Say no more!
We all have heard of so-called alternative therapies but few of us are aware of the fact that there are also alternative diagnoses. These are diagnoses used regularly by practitioners of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) that have no basis on science, or – to put it simply – that do not exist. They are nonetheless popular with SCAM practitioners and allegedly cause a wide range of non-specific symptoms such as:
- anxiety,
- brain fog,
- constipation,
- depression,
- dizziness,
- fatigue,
- headaches,
- heart palpitations,
- insomnia,
- irritability,
- muscle and joint pain,
- loss of appetite,
- loss of libido,
- weight gain.
In this series of posts, I will briefly discuss some of these diagnoses and list the treatments that SCAM practitioners might recommend for them.
Adrenal Fatigue
Adrenal fatigue is not the same as adrenal insufficiency or Addison’s disease; it is a term coined by a chiropractor who claimed that the stresses of modern life tire out the adrenal glands. In turn, this phenomenon allegedly leads to generalised weariness.
There is not evidence that this is true, nor that adrenal fatigue even exists. A systematic review of the evidence concluded that “there is no substantiation that adrenal fatigue is an actual medical condition.”
Yet, SCAM practitioners advise to cure adrenal fatigue with a range of dietary supplements (e.g. fish oil, ashwagandha, rhodiola rosea, schisandra and holy basil, licorice, magnesium, various vitamins), special diets, lifestyle adjustments, stress management and many other SCAMs. They all have in common that their effectiveness is not supported by convincing evidence from rigorous clinical trials.
Candidiasis hypersensitivity
Most of us are infected by the fungus Candida albicans without being affected by it in any way. Yet, many SCAM practitioners claim that candidiasis hypersensitivity is a condition that causes symptoms like fatigue, premenstrual tension, gastrointestinal symptoms, and depression and therefore needs treating.
But, candidiasis hypersensitivity does not exist. An RCT concluded that, “in women with presumed candidiasis hypersensitivity syndrome, nystatin does not reduce systemic or psychological symptoms significantly more than placebo.”
This, however, does not stop SCAM practitioners to recommend numerous forms of SCAM to treat the condition, e.g.: dietary supplements containing probiotics, milk thistle, red thyme, barberry, garlic, or external applications of coconut oil, essential oils of peppermint oil, lavender oil, oregano oil, and tea tree. No sound evidence exists to show that ant of these SCAMs can successfully treat the condition.
Chronic intoxications
Chronic intoxications do ecist, of course. But in the realm of SCAM, they are diagosed for the sole putpose of selling their various ‘detox’ treatments. The alleged rationale is that our bodies are overloaded with all sorts ot harmful substances, for instance, from the environment, from our food, from modern drugs, or from our own metabolism.
To eliminate them, we need to ‘detox’. For that purpose, SCAM practitioners recommend a very wide range of SCAMs; in fact, it is hardly possible to identify a single form of SCAM that is not said to detoxify our bodies. Yet, for none of them is there compelling evidence that it eliminates toxins from our body. Some of the most popular detox regimen include:
- acupuncture;
- CEASE therapy;
- chelation therapy;
- crystal healing;
- cupping;
- detox diets;
- detox supplements;
- gua sha;
- homeopathy;
- homotoxicology;
- Kombucha;
- oil pulling;
- vaginal steaming.
Interim conclusion: non-existing diagnoses are perfect opportunities for SCAM practitioners to rip off gullible patients.
It has been reported that 5 people who took a Japanese health supplement have died and more than 100 have been hospitalized as of Friday, a week after a pharmaceutical company issued a recall of the products, officials said. Osaka-based Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co. came under fire for not going public quickly with problems known internally as early as January. Yet the first public announcement came only on 22 March. Company officials said 114 people were being treated in hospitals after taking products — including Benikoji Choleste Help meant to lower cholesterol — that contain an ingredient called benikoji, a red species of mold. Some people developed kidney problems after taking the supplements, but the exact cause was still under investigation in cooperation with government laboratories, according to the manufacturer.
“We apologize deeply,” President Akihiro Kobayashi told reporters last Friday, bowing for a long time to emphasize the apology alongside three other top company officials. He expressed remorse to those who have died and have been taken ill and to their families. He also apologized for the troubles caused to the entire health food industry and the medical profession, adding that the company was working to prevent further damage and improve crisis management.
The company’s products have been recalled — as have dozens of other products that contain benikoji, including miso paste, crackers, and a vinegar dressing. Japan’s health ministry put up a list on its official site of all the recalled products, including some that use benikoji for food coloring. The ministry warned the deaths could keep growing. The supplements could be bought at drug stores without a prescription from a doctor, and some may have been purchased or exported before the recall, including by tourists who may not be aware of the health risks.
Kobayashi Pharmaceutical had been selling benikoji products for years, with a million packages sold over the past 3 fiscal years, but a problem crept up with the supplements produced in 2023. Kobayashi Pharmaceutical said it produced 18.5 tons of benikoji last year. Some analysts blame the recent deregulation initiatives, which simplified and sped up approval for health products to spur economic growth.
________________________
Anouther source reported that Japanese authorities on Saturday raided a drug factory after a pharmaceutical company reported at least five deaths and 114 hospitalizations possibly linked to a health supplement. About a dozen Japanese health officials walked into the Osaka plant of the Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co., as seen in footage of the raid widely telecasted on Japanese news. The health supplement in question is a pink pill called Benikoji Choleste Help. It is said to help lower cholesterol levels. A key ingredient is benikoji, a type of red mold. The company has said it knows little about the cause of the sickness, which can include kidney failure. It is currently investigating the effects in cooperation with Japan’s government.
___________________________
More recent reports update the figure of affected individuals: Japanese dietary supplements at the center of an expanding health scare have now been linked to at least 157 hospitalizations, a health ministry official said Tuesday.The figure reflects an increase from the 114 hospitalization cases that Kobayashi Pharmaceutical said on Friday were linked to its products containing red yeast rice, or beni kōji.
A Kobayashi Pharmaceutical spokeswoman confirmed the latest hospitalization cases without elaborating further.
Benikoji is widely sold and used; not just in Japan. It comes under a range of different names:
- red yeast rice,
- red fermented rice,
- red kojic rice,
- red koji rice,
- anka,
- angkak,
- Ben Cao Gang Mu.
It is a bright reddish purple fermented rice which acquires its color from being cultivated with the mold Monascus purpureus. Red yeast rice is used as food and as a medicine in Asian cultures, such as Kampo and TCM.
It contains lovastatin which, of course, became patented and is marketed as the prescription drug, Mevacor. Red yeast rice went on to become a non-prescription dietary supplement in the United States and other countries. In 1998, the U.S. FDA banned a dietary supplement containing red yeast rice extract, stating that red yeast rice products containing monacolin K are identical to a prescription drug, and thus subject to regulation as a drug.
Looking at some ancient papers of mine, I came across a short BMJ paper from 1994. Here is a passage from it:
… A standard letter (on departmental letterhead) was written (in German) to all 189 firms that we identified as marketing herbal drugs in Germany. It asked (among other questions) for reprints of articles reporting controlled clinical trials on the company’s product(s).
Only 19 replies had reached us six weeks later. Four of these included at least one reprint. Twelve respondents regretted not knowing of clinical trials on their drug(s). In three cases we had written to a wrong address (one
instance) or to a firm which did not market phytomedicines (two instances).
These data, though far from conclusive, do not give the impression that research is in proportion to either prevalence or financial tumover of herbal remedies…
I wonder what the results would be, if we repeated this little excercise today, 30 years afteer the original investigation. I fear that the findings would be much the same or perhaps even worse. I also suspect that they would be similar regardless of the country we chose. Those who sell herbal remedies have very little incentive to do expensive clinical trials to test whether the products they earn their money with actually work. They may be doing well without it and ask themselves, why spend money on research that might not show what we hope and could easily turn out to jeopardize our financial success?
But the problem is by no means confined to herbal manufacturers (who would arguably have an important share to initiate and sponsor research). Even though fundamental questions remain unanswered, research into herbal medicine is scarce across the board.
To see whether this statement is true, I did a very quick Medline search. It showed that, in 2023, just over 13 000 papers on herbal medicine emerged. Of those, just 460 were listed as clinical trials. The latter figure is almost certainly considerably smaller than the true amount because Medline is over-generous in classifying papers as clinical trials. I thus estimate that only around 200 clinical trials of herbal medicine are conducted each year. Considering that we are dealing with thousands of herbs and ten thousands of herbal products, this figure is an embarrassment for the sector – which, as we have seen just days ago, is doing extremely well in finacial terms.
I usually take ‘market reports’ with a pinch of salt. Having said that, this document makes some rather interesting predictions:
The size of the market for so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) is projected to expand from USD 147.7 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 1489.4 billion by the year 2033. This projection indicates a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 26% over the forecast period.
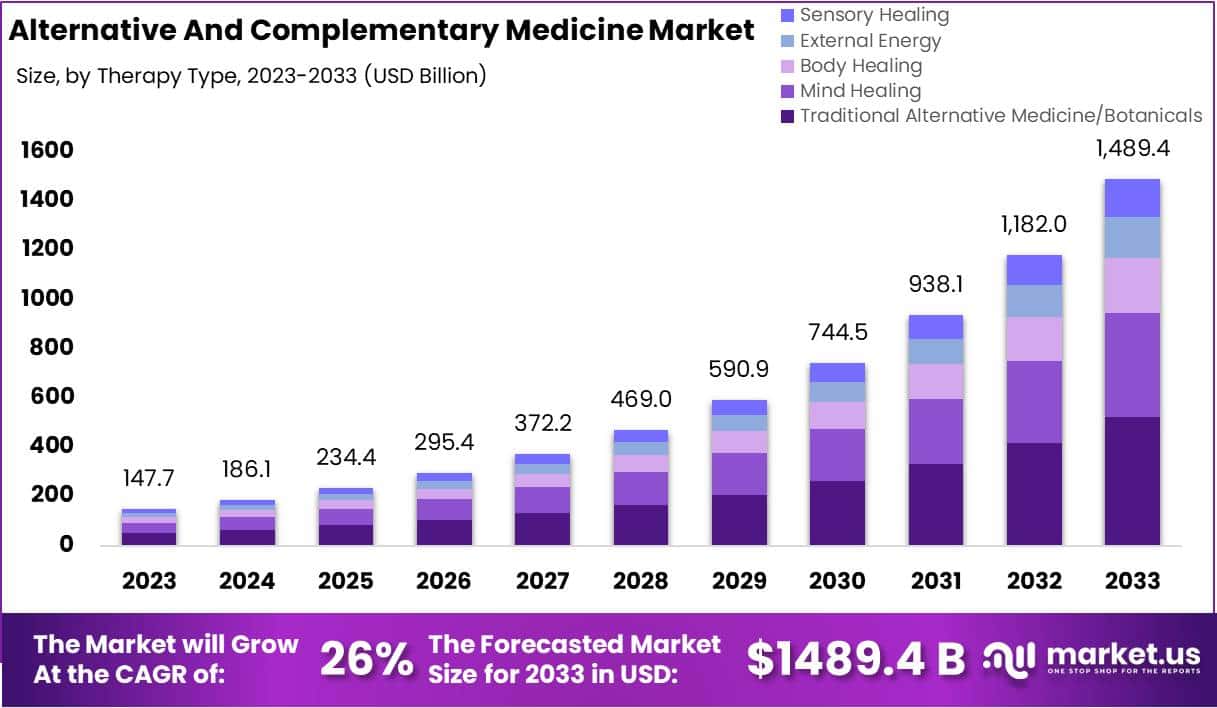
The market for SCAM is experiencing significant growth, fueled by increasing consumer interest in natural and holistic health solutions. This trend reflects a broader shift in societal attitudes towards health and wellness, emphasizing preventive care and natural health practices.
The market’s dynamics are influenced by various factors, including consumer preferences, regulatory standards, and evolving perceptions of health and wellness. As the popularity of these alternative therapies grows, it is crucial for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure that these non-conventional approaches are safely and effectively incorporated into their overall health regimen. The increasing acceptance of SCAM underscores a collective move towards more personalized and holistic healthcare solutions, resonating with today’s health-conscious consumers.
In 2023, Traditional Alternative Medicine/Botanicals led the market, capturing a 35.2% share, which reflects a strong consumer inclination towards these treatments. Dietary Supplements were prominent in the market, securing a 25.1% share in 2023, which underscores the high consumer demand for nutritional aids. Direct Sales were the most favored distribution channel, accounting for 43.2% of the market share in 2023, which indicates their significant impact on guiding consumer purchases. Pain Management was the predominant application area, holding a 24.9% market share in 2023, propelled by the growing acknowledgment of non-pharmacological treatment options. Adults represented a substantial portion of the market, making up 62.33% in 2023, signifying a marked preference for SCAM therapies within this age group. Europe stood out as the market leader, claiming a 42.6% share in 2023, a position supported by widespread acceptance, governmental backing, and an increasing elderly population. The regions of North America and Asia-Pacific are highlighted as areas with potential, signaling opportunities for market expansion beyond the European stronghold in the upcoming years.
Leading Market Players Are:
- Columbia Nutritional
- Nordic Nutraceuticals
- Ramamani Iyengar Memorial Yoga Institute
- The Healing Company Ltd.
- John Schumacher Unity Woods Yoga Centre
- Sheng Chang Pharmaceutical Company
- Pure encapsulations LLC.
- Herb Pharm
- AYUSH Ayurvedic Pte Ltd.
Recent developments:
- In December 2023, Adoratherapy launched the Alkemie Chakra Healing Line, an aromatherapy range aimed at harmonizing the seven chakras.
- Coworth Park introduced the Hebridean Sound Treatment in October 2023, merging traditional Hebridean sounds with guided meditation to offer a novel, restorative wellness experience.
- The World Health Organization released draft guidelines in September 2023 for the safe, effective application of traditional medicines.
- Telehealth services, expanding significantly in August 2023, have broadened the reach of SCAM, enhancing patient access to these treatments.
Traditional herbal medicine (THM) is frequently used in pediatric populations. This is perticularly true in many low-income countries. Yet THM has been associated with a range of adverse events, including liver toxicity, renal failure, and allergic reactions. Despite these concerns, its impact on multi-organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) risk has so far not been thoroughly investigated.
This study aimed to investigate the incidence and predictors of MODS in a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) in Ethiopia, with a focus on the association between THM use and the risk of MODS. It was designed as a single-center prospective cohort study conducted at a PICU in the university of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. The researchers enrolled eligible patients aged one month to 18 years admitted to the PICU during the study period. Data on demographic characteristics, medical history, clinical and laboratory data, and outcome measures using standard case record forms, physical examination, and patient document reviews. The predictors of MODS were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models, with a focus on the association between traditional herbal medicine use and the risk of MODS.
A total of 310 patients were included in the final analysis, with a median age of 48 months and a male-to-female ratio of 1.5:1. The proportion and incidence of MODS were 30.96% (95% CI:25.8, 36.6) and 7.71(95% CI: 6.10, 9.40) per 100-person-day observation respectively. Renal failure (17.74%), neurologic failure (15.16%), and heart failure (14.52%) were the leading organ failures identified. Nearly one-third of patients (32.9%) died in the PICU, of which 59.8% had MODS. The rate of mortality was higher in patients with MODS than in those without. The Cox proportional hazards model identified renal disease (AHR = 6.32 (95%CI: 3.17,12.61)), intake of traditional herbal medication (AHR = 2.45, 95% CI:1.29,4.65), modified Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 (mPIM 2) score (AHR = 1.54 (95% CI: 1.38,1.71), and critical illness diagnoses (AHR = 2.68 (95% CI: 1.77,4.07)) as predictors of MODS.
The authors concluded that the incidence of MODS was high. Renal disease, THM use, mPIM 2 scores, and critical illness diagnoses were independent predictors of MODS. A more than twofold increase in the risk of MODS was seen in patients who used TMH. Healthcare providers should be aware of risks associated with THM, and educate caregivers about the potential harms of these products. Future studies with larger sample sizes and more comprehensive outcome measures are needed.
I do fully agree with the authors about the high usage of herbal and other so-called alternative medicines by children. We have shown that, in the UK the average one-year prevalence rate was 34% and the average lifetime prevalence was 42%. We have furthermore shown that the evidence base for these treatments in children is weak, even more so than for general populations. Finally, we can confirm that adverse effects are far from rare and often serious.
It is therefore high time, I think, that national regulators do more to protect children from SCAM practitioners who are at best uncritical about their treatments and at worse outright dangerous.
An alarming story of research fraud in the area of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) is unfolding: Bharat B. Aggarwal, the Indian-American biochemist who worked at MD Anderson Cancer Center, focused his research on curcumin, a compound found in turmeric, and authored more than 125 Medline-listed articles about it. They reported that curcumin had therapeutic potential for a variety of diseases, including various cancers, Alzheimer’s disease and, more recently, COVID-19.
The last of these papers, entitled “Curcumin, inflammation, and neurological disorders: How are they linked?”, was publiched only a few months ago. Here is its abstract:
Background: Despite the extensive research in recent years, the current treatment modalities for neurological disorders are suboptimal. Curcumin, a polyphenol found in Curcuma genus, has been shown to mitigate the pathophysiology and clinical sequalae involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: We searched PubMed database for relevant publications on curcumin and its uses in treating neurological diseases. We also reviewed relevant clinical trials which appeared on searching PubMed database using ‘Curcumin and clinical trials’.
Results: This review details the pleiotropic immunomodulatory functions and neuroprotective properties of curcumin, its derivatives and formulations in various preclinical and clinical investigations. The effects of curcumin on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), brain tumors, epilepsy, Huntington’s disorder (HD), ischemia, Parkinson’s disease (PD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and traumatic brain injury (TBI) with a major focus on associated signalling pathways have been thoroughly discussed.
Conclusion: This review demonstrates curcumin can suppress spinal neuroinflammation by modulating diverse astroglia mediated cascades, ensuring the treatment of neurological disorders.
The Anderson Cancer Center initially appeared to approve of Aggarwal’s work. However, in 2012, following concerns about image manipulation raised by pseudonymous sleuth Juuichi Jigen, MD Anderson Cancer Center launched a research fraud probe against Aggarwal which eventually led to 30 of Aggarwal’s articles being retracted. Moreover, PubPeer commenters have noted irregularities in many publications beyond the 30 that have already been retracted. Aggarwal thus retired from M.D. Anderson in 2015.
Curcumin doesn’t work well as a therapeutic agent for any disease – see, for instance, the summary from Nelson et al. 2017:
“[No] form of curcumin, or its closely related analogues, appears to possess the properties required for a good drug candidate (chemical stability, high water solubility, potent and selective target activity, high bioavailability, broad tissue distribution, stable metabolism, and low toxicity). The in vitro interference properties of curcumin do, however, offer many traps that can trick unprepared researchers into misinterpreting the results of their investigations.”
Despite curcumin’s apparent lack of therapeutic promise, the volume of research produced on curcumin grows each year. More than 2,000 studies involving the compound are now published annually. Many of these studies bear signs of fraud and involvement of paper mills. As of 2020, the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) has spent more than 150 million USD funding projects related to curcumin.
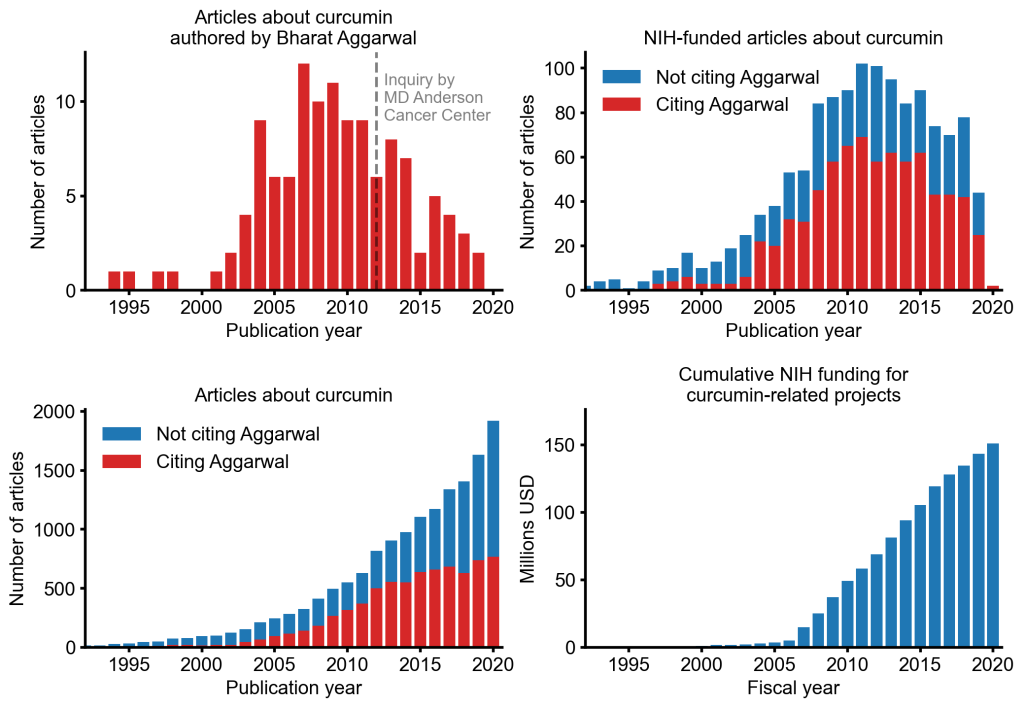
This proliferation of research has fueled curcumin’s popularity as a dietary supplement. It is estimated that the global market for curcumin as a supplement is around 30 million USD in 2020.
The damage done by this epic fraud is huge and far-reaching. Hundreds of millions of taxpayer dollars, countless hours spent toiling by junior scientists, thousands of laboratory animals sacrificed, thousands of cancer patients enrolled in clinical trials for ineffective treatments, and countless people who have eschewed effective cancer treatment in favor of curcumin, were encouraged by research steeped in lies.
The so-called ‘Miracle Mineral Solution’ (MMS) – bleach for you and me – is a SCAM that keeps on giving. On this blog, we have featured MMS several times before, e.g.:
- Selling bleach as ‘miracle’ cure (MMS): Father and three sons are going to prison
- Selling bleach solution as ‘miracle’ cure? No, it’s a dangerous ‘snake oil’!
- Miracle Mineral Supplement (MMS): accidental ingestion by an infant
- Beware of the ‘Bleach Boys’ – hydrogen peroxide and chlorine dioxide
Now,it has been reported that a New Zealand anti-vaxxer has been jailed for selling more than $100,000 worth of an industrial bleach as a “miracle” cure for Covid-19. Roger Blake, who describes himself as a “human man”, was sentenced to just over 10 months’ imprisonment after being found guilty at trial of 29 charges in the Hamilton District Court.
Blake advertised and sold MMS products, claiming it could treat, prevent and cure coronavirus. However, New Zealand’s Ministry of Health had not approved the product, and detailed that when ingested became chlorine dioxide – a bleach commonly used for water treatment, bleaching textiles and paper.
 The court heard Blake had marketed the product as a cure in New Zealand from the start of the pandemic between December 2019 and December 2020. Medsafe, the health ministry’s safety authority, said Blake’s company had sales of NZ$160,000 in that period – with sales spiking in March when the country was placed in lockdown.
The court heard Blake had marketed the product as a cure in New Zealand from the start of the pandemic between December 2019 and December 2020. Medsafe, the health ministry’s safety authority, said Blake’s company had sales of NZ$160,000 in that period – with sales spiking in March when the country was placed in lockdown.
Judge Brett Crowley said Blake’s behaviour had been “utterly disgraceful”. He added that Blake had “seized upon the tragedy” of the pandemic for financial gain. Before selling MMS as a “cure” for the coronavirus, Blake had marketed the product as a preventive of other diseases and illnesses such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, diabetes and HIV.
Medsafe prosecuted him under the Medicines Act, with compliance manager Derek Fitzgerald saying the “fake cure” Blake spruiked presented a “significant public health risk”. “He targeted the vulnerable, preyed on public fears and exposed people to harm”, he said. “This decision sends a strong message that people who engage in selling so called ‘miracle cures’ will be held to account and face fines or imprisonment.”
The website which sold MMS in New Zealand was registered to US-based Mark Grenon, who set up the “Genesis II Church of Health and Healing”. As reported previously, Grenon and his three sons were jailed in October for several years in the US for selling more than US$1m of the product. Michael Homer, an assistant US lawyer who prosecuted the case, said at the time the family targeted people suffering from life-threatening illnesses. The Grenons poisoned thousands of people with their bogus miracle cure, which was nothing more than industrial bleach,” he said.
Medsafe warns: “Drinking MMS is the same as drinking bleach and can cause dangerous side effects, including severe vomiting, diarrhoea, and life-threatening low blood pressure. We strongly encourage people to only go to trusted sources, such as your doctor, to get reliable information”.
Medsafe received three reports of people requiring hospitalizations after drinking MMS. “His conduct presented a significant risk to public health, and that is why Medsafe acted. His actions were in stark contrast to the requirements of the Medicines Act 1981, which is public welfare legislation designed to protect the public” said Mr Fitzgerald.
Mushrooms are somewhat neglected in medical research, I often feel. This systematic review focused on clinical studies testing the effectiveness of mushrooms in cancer care. A total of 39 met the authors’ inclusion criteria. The studies included 12 different mushroom preparations. Some of the findings were encouraging:
- A survival benefit was reported using Huaier granules (Trametes robiniophila Murr) in 2 hepatocellular carcinoma studies and 1 breast cancer study.
- A survival benefit was also found in 4 gastric cancer studies using polysaccharide-K (polysaccharide-Kureha; PSK) as an adjuvant therapy.
- Eleven studies reported a positive immunological response.
- Quality-of-life (QoL) improvement and/or reduced symptom burden was reported in 14 studies using various mushroom supplements.
- Most studies reported adverse effects of grade 2 or lower, mainly nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and muscle pain.
The authors caution that limitations included small sample size and not using randomized controlled trial design. Many of the reviewed studies were observational. Most showed favorable effects of mushroom supplements in reducing the toxicity of chemotherapy, improving QoL, favorable cytokine response, and possibly better clinical outcomes.
The authors concluded that the evidence is inconclusive to recommend the routine use of mushrooms for cancer patients. More trials are needed to explore mushroom use during and after cancer treatment.
The use of mushrooms for medicinal purposes has a long history in many cultures. Some mushrooms are known to be highly poisonous, some have hallucinogenic effects, and some are assumed to have pharmacological effects that have therapeutic potential. Some mushrooms possess pharmacologic properties such as anti-tumour, immunomodulating, antioxidant, cardiovascular, anti-hypercholesterolemic, anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-parasitic, anti-fungal, detoxification, hepatoprotective, and anti-diabetic effects.
Many modern medicines were derived from fungi. The best-known example is penicillin; others include several cancer drugs, statins and immunosuppressants. In Traditional Chinese Medicine, numerous herbal mixtures contain mushrooms; examples are reishi, maitake and shiitake which are all assumed to have anti-cancer properties.
As the review authors point out, there is a paucity of clinical trials testing the effectiveness of mushrooms, and the existing studies tend to be of poor quality. At present, most of our knowledge comes from traditional use or test-tube studies. The adverse effects depend on the specific mushroom in question and, can in some instances, be serious.
Considering the potential and the complexity of mycomedicine, I find it surprising to not see much more research into this subject.
Despite effective vaccines, there is still a need for effective treatments for COVID, especially for people in the community. Dietary supplements have long been used to treat respiratory infections, and preliminary evidence indicates some may be effective in people with COVID-19. This study tested whether a combination of vitamin C, vitamin D3, vitamin K2 and zinc would improve overall health and decrease symptom burden in outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Participants were randomised to receive either vitamin C (6 g), vitamin D3 (1000 units), vitamin K2 (240 μg) and zinc acetate (75 mg) or placebo daily for 21 days and were followed for 12 weeks. An additional loading dose of 50 000 units vitamin D3 (or placebo) was given on day one. The primary outcome was participant-reported overall health using the EuroQol Visual Assessment Scale summed over 21 days. Secondary outcomes included health status, symptom severity, symptom duration, delayed return to usual health, frequency of hospitalisation and mortality.
A total of 90 patients (46 control, 44 treatment) were randomised. The study was stopped prematurely due to insufficient capacity for recruitment. The mean difference (control-treatment) in cumulative overall health was -37.4 (95% CI -157.2 to 82.3), p=0.53 on a scale of 0-2100. No clinically or statistically significant differences were seen in any secondary outcomes.
The authors concluded that, in this double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial of outpatients diagnosed with COVID-19, the dietary supplements vitamin C, vitamin D3, vitamin K2 and zinc acetate showed no clinically or statistically significant effects on the documented measures of health compared with a placebo when given for 21 days. Termination due to feasibility limited our ability to demonstrate the efficacy of these supplements for COVID-19. Further research is needed to determine clinical utility.
In several ways I am puzzled by this study. On the other hand, I should congratulate the naturopathic authors for honestly reporting such a squarely negative result. One could, of course, argue that the study was under-powered and that thus the findings are not conclusive. However, the actual survival curve depicting the results show clearly that there was not even the tiniest trend for the supplement to show any effect. In other words, a larger sample would have most likely yielded the same result.
Participants randomised to the treatment arm received:
- Vitamin D3 50 000 units orally once on day 1 of the study (capsule).
- Vitamin K2/D3 120 μg/500 units orally two times per day for 21 days (liquid).
- Vitamin C/Zinc acetate 2 g/25 mg orally three times daily for 21 days (capsule).
I fail to understand why the researchers might have conceived the hypothesis that such a mixture would be effective. Only 90 of a planned 200 participants were enrolled in this study which ran between September 2021 and April 2022. I fail to understand why recruitment was so poor that the study eventually had to be aborted. My speculation is that the naturopaths in charge of running the trial were too inexperienced in conducting such research to make it a success.
The study was supported by the Ottawa Integrative Cancer Centre Foundation and by Mavis and Martin Sacher. All investigational products for this study were provided in-kind by New Roots Herbal. Perhaps in future these sponsors should think again before they support amateurs pretending to be scientists?
