prevention
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of spiritually based interventions on blood pressure (BP) among adults. A systematic search was performed using the PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane databases to identify studies evaluating spiritual interventions, including:
- meditation,
- transcendental meditation,
- mindfulness meditation,
- yoga,
for high BP among adults up to January 1, 2022.
The inclusion criteria were:
- (a) randomized controlled trials (RCTs),
- (b) studies in English or Persian,
- (c) studies conducted among adults (≥ 18 years),
- (d) studies reporting systolic or diastolic BP.
Given the high heterogeneity of these studies, a random effect model was used to calculate the effect sizes for the RCTs.
In total, the systematic review included 24 studies and the meta-analysis included 23 studies. As some of studies reported two or more outcome measurements, separate estimates of each outcome were extracted for that study (24 datasets). Fifteen trials reported the mean (SD) systolic blood pressure (SBP), and 13 trials reported the mean (SD) diastolic blood pressure (DBP). In addition, 13 studies reported means (SDs) and six trials reported mean changes in DBP. A significant decrease was found in systolic BP following intervention ((WMD (weighted mean difference) = − 7.63 [− 9.61 to − 5.65; P < 0.001]). We observed significant heterogeneity among the studies (I2 = 96.9; P < 0.001). A significant decrease was observed in DBP following the interventions (WMD = − 4.75 [− 6.45 to − 3.05; P < 0.001]).
The authors concluded that spiritually based interventions including meditation and yoga had beneficial effects in reducing both SBP and DBP. Reducing BP can be expected to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Q: What do the RCTs of these interventions have in common?
A: They cannot normally be placebo-controlled because no adequate placebos exist for these therapies.
Q: What does that mean?
A: It means that patients could not be blinded and that patient expectations influenced the outcome.
In view of the fact that blood pressure is an endpoint that is extremely sensitive to expectation, I think, the conclusions of this paper might need to be re-formulated:
This analysis confirms that expectation can have beneficial effects in reducing both SBP and DBP. Reducing BP can be expected to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Pre-diabetes is a significant public health problem worldwide. India has a very high rate of progression from pre-diabetes to diabetes, 75-78 per thousand persons per year.
The objective of this study was to test the efficacy of individualized homeopathic medicinal products (HMPs) against placebos in preventing the progression from pre-diabetes to diabetes. It was designed as a ix-month, double-blind, randomized (1:1), two parallel arms, placebo-controlled trial.
Sixty participants with pre-diabetes were treated either with:
- HMPs plus yoga therapy (YT; n = 30)
- or with identical-looking placebos plus YT (n = 30).
Pre-diabetes was defined as elevated fasting blood glucose (FBS) of 100-125 mg/dL, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) value of 5.7-6.4%, and/or an elevated blood glucose level 2 hrs. after an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) of 140-199 mg/dL (ICD-10-R73.03).
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants progressing from pre-diabetes to diabetes, measured after three and six months. Secondary outcomes comprised of fasting blood glucose (FBS), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), glycated hemoglobin percentage (HbA1c%), lipid profile, liver enzymes (alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminase), urea and creatinine, and Measure Yourself Medical Outcome Profile version 2 (MYMOP-2); all measured after 3 and 6 months.
The proportion of participants converted from pre-diabetics to diabetics (n/N; n = diabetics, N = prediabetics) was significantly less in the verum group than control: HbA1C% (month 3: verum – 2/30 versus control – 11/30, p = 0.003; month 6: 3/30 vs. 2/30, p = 0.008), OGTT (month 3: 0/30 vs. 8/30, p = 0.015; month 6: 0/30 vs. 1/30, p = 0.008), but not according to FBS (month 3: 1/30 vs. 1/30, p = 0.779; month 6: 1/30 vs. 3/30, p = 0.469). Several secondary outcomes also revealed significant improvements in the verum group than in placebo: HbA1C% (p < 0.001), OGTT (p = 0.001), serum ALT (p = 0.031), creatinine (p = 0.012), and MYMOP-2 profile scores (p < 0.001). Sulphur, Bryonia alba, and Thuja occidentalis were the most frequently indicated medicines. Thus, HMPs outperformed placebos by successfully preventing the progression of pre-diabetes to diabetes.
The authors concluded that HMPs with YT produced significantly better effects than placebos plus YT with moderate to large effect sizes. Overall, HMPs outperformed placebos by successfully preventing the progression of pre-diabetes to diabetes.
This is an odd study with very odd results; it begs several questions and comments, e.g.:
- If the aim was to test the efficacy of individualized homeopathic medicinal products (HMPs) against placebos in preventing the progression from pre-diabetes to diabetes, why add yoga as a treatment?
- What were the influences of other factors such as diet and life-style, and were these the same in both groups?
- The sample size seems far too small for such firm conclusions.
- What might be the alleged mechanism of action?
- Why not publish such a study that has allegedly important results in one of the many established journals dealing with diabetes?
I fear that this trial is merely one in the long list of poor quality, false-positive homeopathy studies that are currently emerging from India. I predict that the findings will not even be taken seriously enough to be submitted to a replication by established diabetes researchers.
An interesting and fully referenced (205 references) article caught my attention; it seems highly relevant to the discussions we are having on this blog. Let me show you the abstract:
Medical misinformation has always existed, but it has recently become more frequent due to the development of the internet and social media. Medical misinformation can cover a wide variety of topics, and studies show that some groups are more likely to be affected by medical misinformation than others, like those with less trust in health care, less health literacy, and a more positive attitude toward alternative medicines. Aspects of the internet, like echo chambers and algorithms, have contributed to the rise of medical misinformation, along with belief in anecdotal evidence and alternative remedies that are not backed by science. Some personal beliefs and a lack of media literacy skills are also contributing to medical misinformation. Medical misinformation causes higher rates of death and negative health outcomes, a lack of trust in medical professionals, and more racism and hate crimes. One possible way to combat the spread of misinformation is education surrounding media literacy. Still, there are gaps in this practice that must be addressed like a lack of high-quality research about different educational programs.
The author also offers the following key points:
- Medical misinformation is becoming an urgent issue for United States citizens—leading to increased deaths,
a lack of trust in health professionals, and hate crimes and racism. - Although this is a worldwide issue, the United States has the second highest rate of misinformation of any
country, behind India. - One piece of misinformation during the COVID-19 pandemic stated that highly concentrated alcohol could
disinfect the body and kill the virus. Studies show that 800 people died, 5,876 were hospitalized, and 60
became completely blind from drinking methanol, thinking it would cure coronavirus. - Studies estimate that only 14% of the United States population has proficient health literacy, which makes it difficult to recognize medical misinformation.
- Media literacy education is being pursued in order to combat the spread of misinformation, but more research is needed in order to understand the long-term effects of this education and what programs are best.
__________________
I would like to stress, as indeeed the author does as well, that medical misinformation is a phenomenon that is by no means confined to the US. Like most information, misinformation has become a global issue. Its dangers cannot be under-estimated. My blog offers an abundance of reports where misinformation in the realm of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) has caused harm and even death. The author advocates media literacy as a remedy for the problem. I would argue that even more important would be to teach CRITICAL THINKING, a task that has to start at school and must continue well into adult life.
This conclusion is so very obvious that it begs an important question: WHY HAS IT NOT BEEN DONE YEARS AGO? The answer, I fear, is simple: for reasons that are self-evident, governments have little interst in the public being able to think critically. On the contrary, governments across the world foremost want to be re-elected, and critical thinking would be a major obstacle to this aim.
In spite of the safety and efficiency of the COVID-19 vaccines and the many promotion efforts of political and expert authorities, a fair portion of the population remained hesitant if not opposed to vaccination. Public debate and the available literature point to the possible role of people’s attitudes towards medical institutions as well as their preference for so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) on their motivations and intentions to be vaccinated. Other potential ideological factors are beliefs about environmental laissez-faire and divine providence insofar as they encourage people to let the pandemic unfold without human interference.
In three cross-sectional samples (total N = 8214), collected at successive moments during the Belgian vaccination campaign, the present research examines the distal role of these psychological and ideological factors on vaccination intentions via motivational processes.
- Study 1 gauges the relation between trust in medical institutions and preference for SCAM on intentions to get vaccinated via motivations.
- Study 2 examines the role of beliefs in the desirability of letting nature take its course (‘environmental laissez-faire beliefs’) on vaccination intention via motivations.
- Study 3 tests whether people’s adherence to environmental laissez-faire and beliefs about divine providence are linked to their motivations for vaccination via trust in the medical institutions and SCAM.
The results show that adherence to SCAM has a deleterious effect on vaccination intentions, whereas trust in medical institutions has a positive effect. Both ideological factors pertaining to external control are only moderately related, with environmental laissez-faire beliefs having stronger effects on SCAM, medical trust and vaccination motivations.
The evidence of an association between SCAM and willingness to get vaccinated is undeniable. On this blog, we have discussed it repeatedly, e.g.:
- Use of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) and its association with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination status
- Intelligence, Religiosity, SCAM, Vaccination Hesitancy – are there links?
- Andrew Wakefield, Donald Trump, SCAM, and the anti-vaccination cult
- Measles are back – not least thanks to so-called alternative medicine (SCAM), I fear
- Reasons for parental hesitancy or refusal of childhood vaccination
- Endorsement of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) and vaccine hesitancy among physicians
- Are people who oppose COVID-19 vaccinations intellectually challenged?
- So-called alternative medicine (SCAM) and vaccine hesitancy among physicians: findings from Germany, Finland, Portugal, and France
- Interest in so-called alternative medicine is linked to vaccination coverage
- Misinformation and conspiratorial thinking are at the heart of so-called alternative medicine(SCAM)
- Vaccination rates of Canadian healthcare professionals: those of chiropractors and naturopaths are at the lowest
- Echo chambers of vaccine hesitancy and so-called alternative medicine (SCAM)
- Preference of so-called alternative medicine predicts negative attitudes to vaccination
- What are the reasons for opposing COVID vaccinations?
- Anti-vax arguments used by proponents of SCAM are stupid, or wrong, or both
But what exactly is the nature of this association?
- Does SCAM-use predispose to vaccination hesitancy?
- Does Vaccination hesitancy predispose to SCAM use?
- Is both true?
After reading all this research that has emerged on the subject, I get the impression that we are mostly dealing here with a cross-correlation where a certain mind-set of being
- prone to conspiracy theories,
- anti-establishment,
- anti-science,
- irrational,
- of low intelligence,
- unable of critical thinking,
- etc., etc,
determines both the SCAM-use and the vaccination hesitancy.
This study aims to assess the feasibility of a pragmatic prospective study aiming to report the immediate and delayed (48-hours post-treatment) AEs associated with manual therapies in children aged 5 or younger and to report preliminary data on AEs frequency.
Between July 2021 and March 2022, chiropractors were recruited through purposive sampling and via a dedicated Facebook group for Quebec chiropractors interested in pediatrics. Legal guardians of patients aged 5 or younger were invited to fill out an online information and consent form. AEs were collected using the SafetyNET reporting system, which had been previously translated by the research team. Immediate AEs were collected through a questionnaire filled out by the legal guardian immediately after the treatment, while delayed AEs were collected through a questionnaire sent by email to the legal guardian 48 h after the treatment. Feasibility was assessed qualitatively through feedback from chiropractors and quantitatively through recruitment data.
Overall, a total of 28 chiropractors expressed interest following the Facebook publication, and 5 participated. An additional two chiropractors were enrolled through purposive sampling. In total, 80 legal guardians consented to their child’s participation, and data from 73 children were included for the analysis of AEs. At least one AE was reported in 30% of children (22/73), and AEs were mainly observed immediately following the treatment (16/22). The most common AEs were irritability/crying (11 children) or fatigue/tiredness (11 children). Feasibility analysis demonstrated that regular communication between the research team and clinicians, as well as targeting clinicians who showed great interest in pediatrics, were key factors for successful research.
The authors concluded that their results suggest that it is feasible to conduct a prospective pragmatic study evaluating AEs associated with manual therapies in private practices. Direct communication with the clinicians, a strategic clinicians’ recruitment plan, and the resulting administrative burden should be considered in future studies. A larger study is required to confirm the frequency of AEs reported in the current study.
It is hardly surprising that such a study is ‘feasible’. I could have told the authors that and saved them the trouble of doing the study. What is surprising, in my view, that chiropractors, after ~120 years of existence of the profession, ask whether it is feasible.
I suggest to do the definitive study on a much larger sample, extend the observation period, and recruit a representative rather than self-selected sample of chiros … or – much better – forget about the study and establich a functioning post-marketing surveillance system.
The Amercian Medical Association (AMA) recently published a lengthy article on naturopathy in the US. Here are some excerpts:
There are three types of health professionals who offer naturopathic treatment:
- Naturopathic doctors. These nonphysicians graduate from a four-year, professional-level program at an accredited naturopathic medical school, earning either the doctor of naturopathy (ND) degree or the doctor of naturopathic medicine (NMD) degree.
- Traditional naturopaths, who have obtained education through some combination of a mentorship program with another professional or at an alternative clinic, distance-learning program or classroom schooling on natural health, or other holistic studies.
- Other health professionals such as chiropractors, massage therapists, dentists, nurses, nutritionists, or physicians who practice under a professional license but include some naturopathic methods in their practice and who may have studied on their own or taken courses on naturopathic methods.
At least 24 states and the District of Columbia regulate the practice of naturopathy. In order to be licensed, naturopaths in these states must earn an ND or NMD from an accredited naturopathic program and pass the Naturopathic Physicians Licensing Exam. Three states—Florida, South Carolina and Tennessee—prohibit the practice of naturopathy. In states that neither license nor prohibit the practice of naturopathy, traditional naturopaths and NDs alike may practice without being subject to state regulation.
Postgraduate training is neither common nor required of graduates of naturopathic schools, except in Utah … less than 10% of naturopaths participate in an approved residency, and such residencies last only a year and lack a high degree of standardization.
… naturopaths are required to get at least 1,200 hours of direct patient contact, physicians get 12,000–16,000 hours of clinical training…
ND programs emphasize naturopathic principes—for example, the healing power of nature—and naturopathic therapeutics such as botanical medicine, homeopoathy and hydrotherapy. Coursework in naturopathic therapeutics is combined with, and taught alongside, coursework in sciences. But there are no specifications around the number of hours required in each area … naturopathic students may lack exposure to key clinical scenarios in the course of their training … naturopathic students’ clinical experience is typically gained through outpatient health care clinics, as naturopathic medical schools typically do not have significant hospital affiliation. This means there is no guarantee that a naturopathic student completing a clinical rotation will see patients who are actually sick or hospitalized, and they may not be exposed to infants, children, adolescents or the elderly. It has been said that naturopaths tend to treat the “worried well.”
… Naturopaths claim they are trained as primary care providers and, as such, are educated and trained to diagnose, manage and treat many conditions, including bloodstream infections, heart disease and autoimmune disorders. Yet their education and training falls several years and thousands of hours short of what physicians get.
…The AMA believes it is the responsibility of policymakers to ensure that naturopaths’ claims that they can treat a broad range of conditions are backed by facts—facts that include the specific education and training necessary to ensure patient safety.
________________
The AMA is clearly cautious here. A less polite statement might simply stress that naturopaths are taught a lot of nonsense which they later tend to administer to their unsuspecting patients. On this blog, we have repeatedly discussed the danger naturopaths present to public health in the US and elsewhere, e.g.:
- How reliable are the claims made by naturopathic influencers?
- Naturopath jailed for selling fraudulent vaccination documents
- Naturopath fined for misdiagnosing and treating a rectal tumor for hemorrhoids
- Naturopaths are ‘not bound by science,’ lawyer argues
- Vaccination rates of Canadian healthcare professionals: those of chiropractors and naturopaths are at the lowest
- Is veterinary naturopathy animal abuse?
- Naturopathic ‘cancer specialist’ using coffee enemas found guilty
- Patients consulting chiropractors, homeopaths, or naturopaths are less likely to agree to the flu jab
- A naturopath responsible for the death of two cancer patients was sentenced to two years
- A naturopath in court after two of his cancer patients died
- Many naturopaths, homeopaths, and chiropractors are a risk to public health
- Naturopath treats autism with fecal transplants
- A naturopath promoting fake news about COVID vaccinations
- Naturopathy (according to the WNF) = quackery steeped in obsolete fantasies
- Canadian naturopaths may no longer call themselves ‘medically trained’
- Naturopaths’ counselling against vaccinations could be criminally negligent
- Naturopathy for cancer … claims that have the potential to be lethal
- Severe liver injury due to naturopaths’ prescription of Epsom salt
- Naturopaths should not treat children
- Some naturopaths are clearly a danger to public health
- Death of a child through naturopathy
Claims that naturopaths are a viable alternative to evidence-based medicine are wrong, irresponsible and dangerous. Regulators must be reminded that they have the duty to protect the public from charlatans and should therefore ensure that no false therapeutic or diagnostic claims can be made by naturopaths.
I usually take ‘market reports’ with a pinch of salt. Having said that, this document makes some rather interesting predictions:
The size of the market for so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) is projected to expand from USD 147.7 billion in 2023 to approximately USD 1489.4 billion by the year 2033. This projection indicates a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 26% over the forecast period.
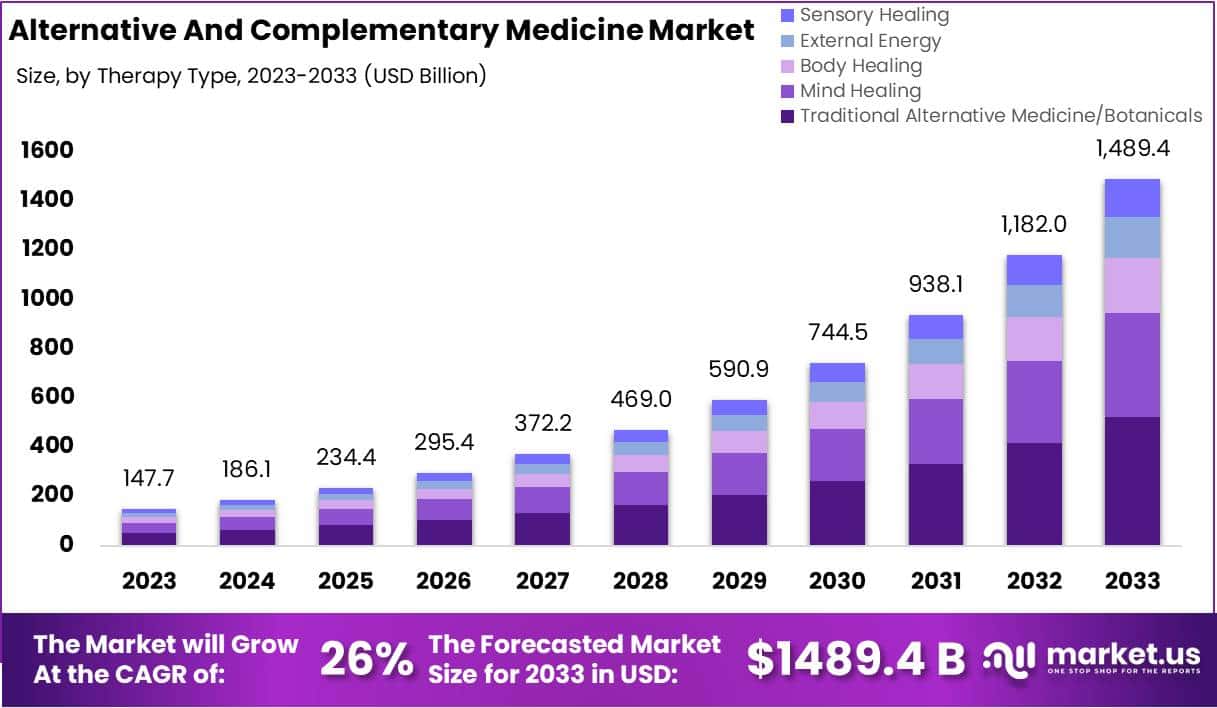
The market for SCAM is experiencing significant growth, fueled by increasing consumer interest in natural and holistic health solutions. This trend reflects a broader shift in societal attitudes towards health and wellness, emphasizing preventive care and natural health practices.
The market’s dynamics are influenced by various factors, including consumer preferences, regulatory standards, and evolving perceptions of health and wellness. As the popularity of these alternative therapies grows, it is crucial for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure that these non-conventional approaches are safely and effectively incorporated into their overall health regimen. The increasing acceptance of SCAM underscores a collective move towards more personalized and holistic healthcare solutions, resonating with today’s health-conscious consumers.
In 2023, Traditional Alternative Medicine/Botanicals led the market, capturing a 35.2% share, which reflects a strong consumer inclination towards these treatments. Dietary Supplements were prominent in the market, securing a 25.1% share in 2023, which underscores the high consumer demand for nutritional aids. Direct Sales were the most favored distribution channel, accounting for 43.2% of the market share in 2023, which indicates their significant impact on guiding consumer purchases. Pain Management was the predominant application area, holding a 24.9% market share in 2023, propelled by the growing acknowledgment of non-pharmacological treatment options. Adults represented a substantial portion of the market, making up 62.33% in 2023, signifying a marked preference for SCAM therapies within this age group. Europe stood out as the market leader, claiming a 42.6% share in 2023, a position supported by widespread acceptance, governmental backing, and an increasing elderly population. The regions of North America and Asia-Pacific are highlighted as areas with potential, signaling opportunities for market expansion beyond the European stronghold in the upcoming years.
Leading Market Players Are:
- Columbia Nutritional
- Nordic Nutraceuticals
- Ramamani Iyengar Memorial Yoga Institute
- The Healing Company Ltd.
- John Schumacher Unity Woods Yoga Centre
- Sheng Chang Pharmaceutical Company
- Pure encapsulations LLC.
- Herb Pharm
- AYUSH Ayurvedic Pte Ltd.
Recent developments:
- In December 2023, Adoratherapy launched the Alkemie Chakra Healing Line, an aromatherapy range aimed at harmonizing the seven chakras.
- Coworth Park introduced the Hebridean Sound Treatment in October 2023, merging traditional Hebridean sounds with guided meditation to offer a novel, restorative wellness experience.
- The World Health Organization released draft guidelines in September 2023 for the safe, effective application of traditional medicines.
- Telehealth services, expanding significantly in August 2023, have broadened the reach of SCAM, enhancing patient access to these treatments.
Microplastics are tiny polymer fragments that range from less than 0.2 inch to 1/25,000th of an inch. Smaller particles are called nanoplastics and are measured in billionths of a metre. Microplastics and nanoplastics (MNPs) are emerging as a potential risk factor for human health and for cardiovascular disease in particular. However, direct evidence that this risk extends to humans has so far been lacking. This investigation is a first step towards filling the gap.
The researchers conducted a prospective, multicenter, observational study involving patients who were undergoing carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. The excised carotid plaque specimens were analyzed for the presence of MNPs with the use of pyrolysis–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, stable isotope analysis, and electron microscopy. Inflammatory biomarkers were assessed with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunohistochemical assay. The primary end point was a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from any cause among patients who had evidence of MNPs in plaque as compared with patients with plaque that showed no evidence of MNPs.
A total of 304 patients were enrolled in the study, and 257 completed a mean (±SD) follow-up of 33.7±6.9 months. Polyethylene was detected in carotid artery plaque of 150 patients (58.4%), with a mean level of 21.7±24.5 μg per milligram of plaque; 31 patients (12.1%) also had measurable amounts of polyvinyl chloride, with a mean level of 5.2±2.4 μg per milligram of plaque. Electron microscopy revealed visible, jagged-edged foreign particles among plaque macrophages and scattered in the external debris. Radiographic examination showed that some of these particles included chlorine. Patients in whom MNPs were detected within the atheroma were at higher risk for a primary end-point event than those in whom these substances were not detected (hazard ratio, 4.53; 95% confidence interval, 2.00 to 10.27; P<0.001).
The authors concluded that, in this study, patients with carotid artery plaque in which MNPs were detected had a higher risk of a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from any cause at 34 months of follow-up than those in whom MNPs were not detected.
This is an impressive study – so much so that I report it here even though it has no connection to so-called alternative medicine, the focus of my blog. The fact that 58% of all plaques contained MNPs seems alarming. The finding that the presence of these MNPs is associated with a poor cardiovascular prognosis seems even more concerning.
MNPs have been found in every environmental compartment on earth. They are ingested not just by humans but by most animals as well. Even though research into these issues is most active, their effects are so far still under-researched and not fully understood.
The authors of the new investigation are rightly cautious: “Our data must be confirmed by other studies and on larger populations,” said Marfella, professor of internal medicine and director of the department of medical and surgical sciences at the University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli in Naples, Italy. “However, our study convincingly highlights the presence of plastics and their association with cardiovascular events in a representative population affected by atherosclerosis.”
Of course, many questions are as yet unanswered but the subject is as worrying as it is important, e.g.:
- Should exposure to MNPs be considered a cardiovascular risk factor?
- What organs in addition to the heart may be at risk?
- How can we reduce exposure?”
I wish I knew the ansers.
Here is the abstract of a recent article that I find worrying:
In 2020, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) challenged the world with a global outbreak that led to millions of deaths worldwide. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the symptomatic manifestation of this virus, which can range from flu-like symptoms to utter clinical complications and even death. Since there was no clear medicine that could tackle this infection or lower its complications with minimal adverse effects on the patients’ health, the world health organization (WHO) developed awareness programs to lower the infection rate and limit the fast spread of this virus. Although vaccines have been developed as preventative tools, people still prefer going back to traditional herbal medicine, which provides remarkable health benefits that can either prevent the viral infection or limit the progression of severe symptoms through different mechanistic pathways with relatively insignificant side effects. This comprehensive review provides scientific evidence elucidating the effect of 10 different plants against SARS-CoV-2, paving the way for further studies to reconsider plant-based extracts, rich in bioactive compounds, into more advanced clinical assessments in order to identify their impact on patients suffering from COVID-19.
The conclusions of this paper read as follows:
…since these 10 herbs hold distinct bioactive compounds with significant properties in vitro and with remarkable benefits to human health, it is possible to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce its symptomatic manifestations by consuming any of these 10 plants according to the recommended dose. The diversity in bioactive molecules between the different plants exerts various effects through different mechanisms at once, which makes it more potent than conventional synthetic drugs. Nonetheless, more studies are needed to highlight the clinical efficacy of these extracts and spot their possible side effects on patients, especially those with comorbidities who take multiple conventional drugs.
I should point out that the authors fail to offer a single reliable trial that would prove or even imply that any of the 10 herbal remedies can effectively treat or prevent COVID infections (to the best of my knowledge, no such studies exist). Laguage like “it is possible to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduce its symptomatic manifestations” is therefore not just misleading but highly dangerous and deeply unethical. Sadly, such evidence-free claims abound in herbal medicine.
I think the journal editor, the peer-reviewer, the authors and their universities ( University of Tripoli in Lebanon, American University of the Middle East, Egaila in Kuwait, University of Balamand, Kalhat, Tripoli in Lebanon, Lebanese University, Tripoli in Lebanon, Aix-Marseille Université in France) should be ashamed to produce such dangerous rubbish.
Traditional herbal medicine (THM) is frequently used in pediatric populations. This is perticularly true in many low-income countries. Yet THM has been associated with a range of adverse events, including liver toxicity, renal failure, and allergic reactions. Despite these concerns, its impact on multi-organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) risk has so far not been thoroughly investigated.
This study aimed to investigate the incidence and predictors of MODS in a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) in Ethiopia, with a focus on the association between THM use and the risk of MODS. It was designed as a single-center prospective cohort study conducted at a PICU in the university of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia. The researchers enrolled eligible patients aged one month to 18 years admitted to the PICU during the study period. Data on demographic characteristics, medical history, clinical and laboratory data, and outcome measures using standard case record forms, physical examination, and patient document reviews. The predictors of MODS were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models, with a focus on the association between traditional herbal medicine use and the risk of MODS.
A total of 310 patients were included in the final analysis, with a median age of 48 months and a male-to-female ratio of 1.5:1. The proportion and incidence of MODS were 30.96% (95% CI:25.8, 36.6) and 7.71(95% CI: 6.10, 9.40) per 100-person-day observation respectively. Renal failure (17.74%), neurologic failure (15.16%), and heart failure (14.52%) were the leading organ failures identified. Nearly one-third of patients (32.9%) died in the PICU, of which 59.8% had MODS. The rate of mortality was higher in patients with MODS than in those without. The Cox proportional hazards model identified renal disease (AHR = 6.32 (95%CI: 3.17,12.61)), intake of traditional herbal medication (AHR = 2.45, 95% CI:1.29,4.65), modified Pediatric Index of Mortality 2 (mPIM 2) score (AHR = 1.54 (95% CI: 1.38,1.71), and critical illness diagnoses (AHR = 2.68 (95% CI: 1.77,4.07)) as predictors of MODS.
The authors concluded that the incidence of MODS was high. Renal disease, THM use, mPIM 2 scores, and critical illness diagnoses were independent predictors of MODS. A more than twofold increase in the risk of MODS was seen in patients who used TMH. Healthcare providers should be aware of risks associated with THM, and educate caregivers about the potential harms of these products. Future studies with larger sample sizes and more comprehensive outcome measures are needed.
I do fully agree with the authors about the high usage of herbal and other so-called alternative medicines by children. We have shown that, in the UK the average one-year prevalence rate was 34% and the average lifetime prevalence was 42%. We have furthermore shown that the evidence base for these treatments in children is weak, even more so than for general populations. Finally, we can confirm that adverse effects are far from rare and often serious.
It is therefore high time, I think, that national regulators do more to protect children from SCAM practitioners who are at best uncritical about their treatments and at worse outright dangerous.
