panacea
Whenever a journalist wants to discuss the subject of acupuncture with me, he or she will inevitably ask one question:
DOES ACUPUNCTURE WORK?
It seems a legitimate, obvious and simple question, particularly during ‘Acupuncture Awareness Week‘, and I have heard it hundreds of times. Why then do I hesitate to answer it?
Journalists – like most of us – would like a straight answer, like YES or NO. But straight answers are in short supply, particularly when we are talking about acupuncture.
Let me explain.
Acupuncture is part of ‘Traditional Chinese Medicine’ (TCM). It is said to re-balance the life forces that determine our health. As such it is seen as a panacea, a treatment for all ills. Therefore, the question, does it work?, ought to be more specific: does it work for pain, obesity, fatigue, hair-loss, addiction, anxiety, ADHA, depression, asthma, old age, etc.etc. As we are dealing with virtually thousands of ills, the question, does it work?, quickly explodes into thousands of more specific questions.
But that’s not all!
The question, does acupuncture work?, assumes that we are talking about one therapy. Yet, there are dozens of different acupuncture traditions and sites:
- body acupuncture,
- ear acupuncture,
- tongue acupuncture,
- scalp acupuncture,
- etc., etc.
Then there are dozens of different ways to stimulate acupuncture points:
- needle acupuncture,
- electroacupuncture,
- acupressure,
- moxibustion,
- ultrasound acupuncture,
- laser acupuncture,
- etc., etc.
And then there are, of course, different acupuncture ‘philosophies’ or cultures:
- TCM,
- ‘Western’ acupuncture,
- Korean acupuncture,
- Japanese acupuncture,
- etc., etc.
If we multiply these different options, we surely arrive at thousands of different variations of acupuncture being used for thousands of different conditions.
But this is still not all!
To answer the question, does it work?, we today have easily around 10 000 clinical trials. One might therefore think that, despite the mentioned complexity, we might find several conclusive answers for the more specific questions. But there are very significant obstacles that are in our way:
- most acupuncture trials are of lousy quality;
- most were conducted by lousy researchers who merely aim at showing that acupuncture works rather that testing whether it is effective;
- most originate from China and are published in Chinese which means that most of us cannot access them;
- they get nevertheless included in many of the systematic reviews that are currently being published without non-Chinese speakers ever being able to scrutinise them;
- TCM is a hugely important export article for China which means that political influence is abundant;
- several investigators have noted that virtually 100% of Chinese acupuncture trials report positive results regardless of the condition that is being targeted;
- it has been reported that about 80% of studies emerging from China are fabricated.
Now, I think you understand why I hesitate every time a journalist asks me:
DOES ACUPUNCTURE WORK?
Most journalists do not have the patience to listen to all the complexity this question evokes. Many do not have the intellectual capacity to comprehend an exhaustive reply. But all want to hear a simple and conclusive answer.
So, what do I say in this situation?
Usually, I respond that the answer would depend on who one asks. An acupuncturist is likely to say: YES, OF COURSE, IT DOES! An less biased expert might reply:
IT’S COMPLEX, BUT THE MOST RELIABLE EVIDENCE IS FAR FROM CONVINCING.
Medical Acupuncture is the name of a quarterly journal published for the ‘American Academy of Medical Acupuncture’ that publishes around 60 pro-acupuncture articles every year. Its editor is Richard C. Niemtzow, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H. Richard is a retired US Air Force colonel who was the first full-time physician acupuncturist in the US Armed Forces. He is probably best known for his invention called ‘BATTLE FIELD ACUPUNCTURE’, a form of ear-acupuncture allegedly reducing pain in emergency situations.
Medline lists 79 papers (mostly published in 3rd class journals such as ‘Medical Acupuncture’) in Niemtzow’s name. Only one of them – 21 years ago – was a clinical trial. Here it is:
Purpose: We performed a pilot trial to assess the response of lower urinary tract symptoms and prostate specific antigen (PSA) to acupuncture in a population of patients biopsy negative for prostate cancer.
Materials and methods: A total of 30 patients were randomly assigned to 1 of 3 study groups, including observation for 3 months with 6 blood samples for PSA at set intervals, 9 sessions of acupuncture in 3 months to points of the kidney-bladder distinct meridian expected to treat the prostate with 6 blood samples for PSA at set intervals and 9 sessions of acupuncture in 3 months to points not expected to treat the prostate with 6 blood samples for PSA at set intervals. The effect of acupuncture on lower urinary tract symptoms was assessed monthly using the International Prostate Symptom Score.
Results: Trend analysis (repeated measures ANOVA) revealed no significant changes in the 3-month period in the randomized arms. Statistical analysis showed p = 0.063 for the International Prostate Symptom Score, p = 0.945 for PSA and p = 0.37 for the free-to-total PSA ratio.
Conclusions: Acupuncture to the kidney-bladder distinct meridian neither relieves lower urinary tract symptoms nor impacts PSA.
Yes, an acupuncture study with a negative result!
Niemtzow has, as far as I can see, never himself conducted a study of ‘battle field acupuncture’. In fact, there only very few trials of ‘battle field acupuncture‘. The most recent (albeit lousy) study even suggest that it is less effective than electroacupuncture (EA): EA was more effective than ‘battle field auricular acupuncture’ at reducing pain severity, but both similarly improved physical and mental health scores.
This does not stop Niemtzow to continue praising acupuncture in dozens of papers, particularly his ‘battle field’ version and especially in his ‘own’ journal. The most recent example has just been published; allow me to present an excerpt to you:
In December of 2023, I had the opportunity to visit the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam. The only day I had for this visit was characterized by a pouring and chilling rain. This did not stop the crowds of people visiting this famous exhibition. I reminded myself that Van Gogh was a troubled spirit. He lived a short tumultuous life characterized by cutting off his left ear lobe and he spent a sojourn in an asylum. Yet, his art emerged in all its beauty and splendor to become famous in the world. Despite all his troubles, he contributed a precious collection of magnificent art. Many individuals would not have surfaced out of personal disorders to produce such a wonderful gift to society. However, history tells us that many sensational contributions originated from people embroiled in mental health illnesses.
Medical Acupuncture published more than 13 years ago the acupuncture ‘‘diagnosis’’ of Vincent Van Gogh. The article, which is worth rereading, discussed the Five-Element pattern associated with the artist’s hallucinations, alcoholism, severe depression, insomnia, anxiety, dizziness, headaches, nightmares, etc. The author, Vera Kaikobad, LAc, stated: ‘‘It is poignant to realize that a few needles in the hands of a skilled acupuncturist may have spared this great artist such torment and perhaps saved his life.’’ Feasibly, in 2024 we should not only examine our patients for their physical complaints; we should venture into their mental health status as well. A back or neck pain is important, but so is anxiety, insomnia, etc. In promoting mental health, we may assist many patients who are perhaps capable of contributing to the well-being of the world. It is our responsibility as acupuncturists not to think of our patients as a neck or back pain, etc.; instead, we must see them as whole persons having spiritual and physical needs that must be addressed.
I feel that, overall, this remarkable effort justifies Niemtzow’s admission to my ALTERNATIVE MEDICINE HALL OF FAME.
WELCOME, RICHARD!
And let me introduce you to the rest of the 24 laureates:
- Helmut Kiene (anthroposophical medicine)
- Helge Franke (osteopathy, Germany)
- Tery Oleson (acupressure , US)
- Jorge Vas (acupuncture, Spain)
- Wane Jonas (homeopathy, US)
- Harald Walach (various SCAMs, Germany)
- Andreas Michalsen ( various SCAMs, Germany)
- Jennifer Jacobs (homeopath, US)
- Jenise Pellow (homeopath, South Africa)
- Adrian White (acupuncturist, UK)
- Michael Frass (homeopath, Austria)
- Jens Behnke (research officer, Germany)
- John Weeks (editor of JCAM, US)
- Deepak Chopra (entrepreneur, US)
- Cheryl Hawk (chiropractor, US)
- David Peters (osteopathy, homeopathy, UK)
- Nicola Robinson (TCM, UK)
- Peter Fisher (homeopathy, UK)
- Simon Mills (herbal medicine, UK)
- Gustav Dobos (various SCAMs, Germany)
- Claudia Witt (homeopathy, Germany/Switzerland)
- George Lewith (acupuncture, UK)
- John Licciardone (osteopathy, US)
An alarming story of research fraud in the area of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) is unfolding: Bharat B. Aggarwal, the Indian-American biochemist who worked at MD Anderson Cancer Center, focused his research on curcumin, a compound found in turmeric, and authored more than 125 Medline-listed articles about it. They reported that curcumin had therapeutic potential for a variety of diseases, including various cancers, Alzheimer’s disease and, more recently, COVID-19.
The last of these papers, entitled “Curcumin, inflammation, and neurological disorders: How are they linked?”, was publiched only a few months ago. Here is its abstract:
Background: Despite the extensive research in recent years, the current treatment modalities for neurological disorders are suboptimal. Curcumin, a polyphenol found in Curcuma genus, has been shown to mitigate the pathophysiology and clinical sequalae involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases.
Methods: We searched PubMed database for relevant publications on curcumin and its uses in treating neurological diseases. We also reviewed relevant clinical trials which appeared on searching PubMed database using ‘Curcumin and clinical trials’.
Results: This review details the pleiotropic immunomodulatory functions and neuroprotective properties of curcumin, its derivatives and formulations in various preclinical and clinical investigations. The effects of curcumin on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), brain tumors, epilepsy, Huntington’s disorder (HD), ischemia, Parkinson’s disease (PD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and traumatic brain injury (TBI) with a major focus on associated signalling pathways have been thoroughly discussed.
Conclusion: This review demonstrates curcumin can suppress spinal neuroinflammation by modulating diverse astroglia mediated cascades, ensuring the treatment of neurological disorders.
The Anderson Cancer Center initially appeared to approve of Aggarwal’s work. However, in 2012, following concerns about image manipulation raised by pseudonymous sleuth Juuichi Jigen, MD Anderson Cancer Center launched a research fraud probe against Aggarwal which eventually led to 30 of Aggarwal’s articles being retracted. Moreover, PubPeer commenters have noted irregularities in many publications beyond the 30 that have already been retracted. Aggarwal thus retired from M.D. Anderson in 2015.
Curcumin doesn’t work well as a therapeutic agent for any disease – see, for instance, the summary from Nelson et al. 2017:
“[No] form of curcumin, or its closely related analogues, appears to possess the properties required for a good drug candidate (chemical stability, high water solubility, potent and selective target activity, high bioavailability, broad tissue distribution, stable metabolism, and low toxicity). The in vitro interference properties of curcumin do, however, offer many traps that can trick unprepared researchers into misinterpreting the results of their investigations.”
Despite curcumin’s apparent lack of therapeutic promise, the volume of research produced on curcumin grows each year. More than 2,000 studies involving the compound are now published annually. Many of these studies bear signs of fraud and involvement of paper mills. As of 2020, the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) has spent more than 150 million USD funding projects related to curcumin.
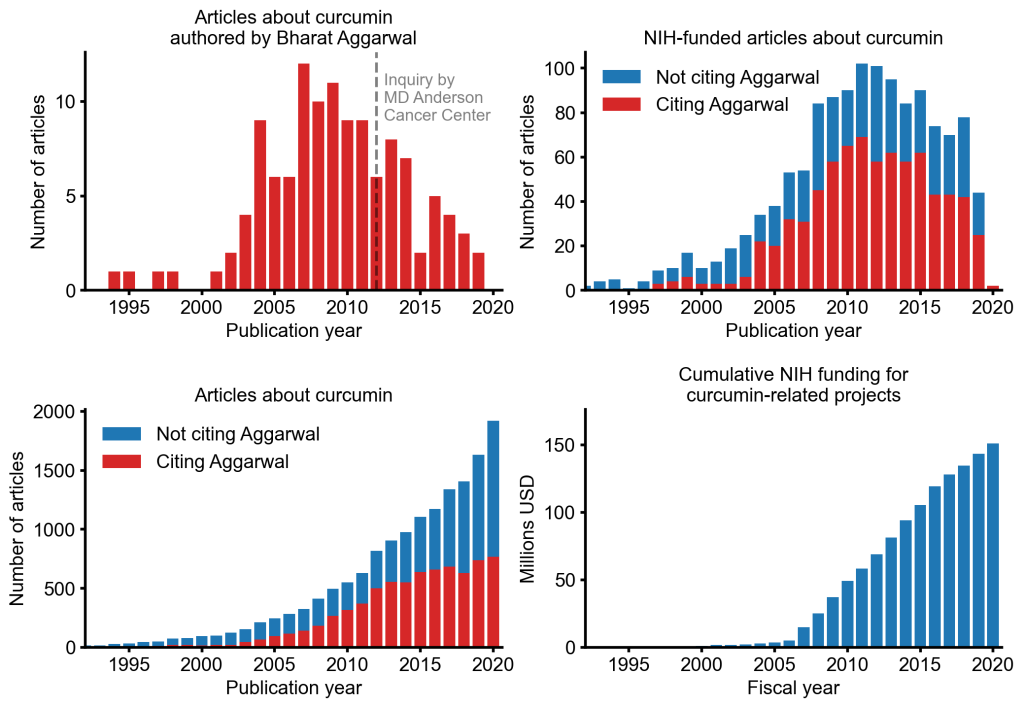
This proliferation of research has fueled curcumin’s popularity as a dietary supplement. It is estimated that the global market for curcumin as a supplement is around 30 million USD in 2020.
The damage done by this epic fraud is huge and far-reaching. Hundreds of millions of taxpayer dollars, countless hours spent toiling by junior scientists, thousands of laboratory animals sacrificed, thousands of cancer patients enrolled in clinical trials for ineffective treatments, and countless people who have eschewed effective cancer treatment in favor of curcumin, were encouraged by research steeped in lies.
I had the rare pleasure to give an interview for the ‘Frankfurter Allgemeine’. As it was, of course, in German, I took the liberty to translate it for my non-German speaking readers:
You have researched so-called alternative medicine over several decades, including homeopathy. What is your conclusion?
We are talking about far more than 400 methods – to draw one conclusion about all of them
is completely impossible. Except perhaps for this one: if something sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
Does this apply to homeopathy?
Highly diluted homeopathic remedies are popular because they have no side-effects. But there is also no effect. They are touted as a panacea. This is certainly not the case, on the contrary, they are
ineffective. And any therapy that is ineffective and promoted as a panacea is also dangerous.
How do you explain the fact that so many people swear by homeopathy?
There are several reasons for this. In Germany, homeopathy has an unbroken tradition, it was, for instance, promoted by the Nazis and later in the Federal Republic of Germany. It has a reputation for being gentle and effective. It might be gentle, but it is certainly not effective. It is also supported by lobby groups such as the manufacturers. And most people who use it don’t even understand what it actually is.
In any case, the placebo effect helps. What’s so bad about that??
Nothing at all, on the contrary: it is to be advocated. When we talk about placebo effects, we subsume many things under this umbrella that do not actually belong to it, such as the extensive, empathetic conversation that homeopaths often have with their patients. Besides, a common cold goes away whether you treat it or not. If you then use homeopathy, you can easily get the impression that it worked. Every good, empathetic doctor tries to maximize the placebo effect. To put it bluntly: you don’t need a placebo to generate a placebo effect. Patients also benefit from it when I give an effective remedy with empathy. In addition they benefit from the specific effect of my therapy, which should make up the lion’s share of the therapeutic response. If I withhold the most important thing I mistreat my patient.
But there are diseases for which there are no good remedies.
I often hear that argument. But there is practically always something we can do that at least
improves symptoms. Otherwise you should also say that instead of lying and recommending homeopathy – and thinking that, although there is nothing in it and it doesn’t work, but the patient, being an idiot, should take it nevertheless. It is unethical to use placebos as much as it is to use homeopathy.
Neurophysiologically, the placebo effect is becoming better and better understood.
The Italian neuroscientist Fabrizio Benedetti in particular has done very good work. But he also warns that this does not justify the use of homeopathy, for example.
Are there any studies on whether the placebo effect of homeopathy with its esoteric superstructure is greater than that giving just a piece of sugar?
There are analyses of what makes a particularly effective placebo. From this, we can learn that effective therapies in evidence-based medicine must be applied with empathy and sufficient time in order to maximize the ever-present placebo effect. So-called alternative medicine often does this quite well, and we can learn something from it. But the reason is that it often has nothing else. Homeopaths are a serious danger because they see homeopathy as a panacea. If someone has homeopathically treated their cold “successfully” for years and then gets cancer, they might think of turning to homeopathy for their cancer. It sounds crazy, but many homeopaths do offer cancer treatments on the internet, for instance. That sends shivers down my spine.
How should doctors and pharmacists react to the demand for homeopathic remedies?
Pharmacists are not primarily salespeople, they are a medical profession – they have to adhere to ethical guidelines. In this respect, evidence-based information of their clients/patients is very important.
Thomas Benkert, President of the German Federal Chamber of Pharmacists, has stated that he would not be able to stop giving advice if he always had to explain the lack of proof of efficacy.
He should perhaps read up on what his ethical duty to patients is.
What if doctors or pharmacists themselves believe in the effect?
Belief should not play a role, but evidence should.
Are you pleased with Lauterbach’s plan to no longer reimburse homeopathy?
I think it’s a shame that he justifies it by saying it’s ineffective. That is true. But the justification should be that it’s esoteric nonsense and therefore ineffective – and dangerous.
In the end, the Bundestag will decide.
I think Lauterbach has a good chance because things have started to move. Medical associations in Germany have spoken out against the additional designation of homeopathy, for example, and overall the wind has changed considerably.
What is it like in the UK, where you live?
The UK healthcare system, NHS, said goodbye to reimbursement of homeopathy about five years ago, even before France. The pharmacists’ association has distanced itself very clearly from homeopathy. However, most pharmacists still sell the remedies and many continue to support them.
You have also had disputes with the current head of state, King Charles. How did that come about?
A few years ago, he commissioned a paper claiming that so-called alternative medicine could save the British health service a lot of money. I protested against this – Charles accused me of leaking it to The Times before it was published. My university launched an investigation, which eventually found me innocent, but it led to the demise of my department. That caused me to retire two years early.
So Charles managed to close down the only research unit in the world that conducted critical and systematic research into so-called alternative medicine. Most researchers in this field only want to confirm their own prejudices and not disprove hypotheses. This is a serious misunderstanding of how science works. If someone reports only positive results for their favorite therapy in all conditions, something is wrong.
Some people say that homeopathy should not be researched because nothing positive can come out of it anyway.
There are certainly some SCAMs that are so nonsensical that they should not be researched, as is currently the case with homeopathy. I put it this way because I have researched homeopathy myself and, from my point of view, the situation was not so crystal clear 30 years ago.
Would you say that you have approached the matter with a sufficiently open mind?
No one can be completely unbiased. That’s why it’s important to do science properly, then you minimize bias as much as possible. When I took up my position at Exeter in 1993, I was perhaps somewhat biased towards homeopathy in a positive sense, because I had learned and used it myself, as well as other alternative medicine methods. The fact that the results then turned out to be negative in the vast majority of cases initially depressed me. But I have to live with that.
Every researcher prefers positive results, also because they are easier to publish. It was clear to me that, if I had succeeded in proving homeopathy right, I wouldn’t get one Nobel Prize, but two. Who wouldn’t want that?
(The interview was conducted by Hinnerk Feldwisch-Drentrup.)
Since the introduction of their new Education Standards in March 2023, the General Chiropractic Council (GCC) has been working with chiropractic education providers to support them in implementing the changes to their curricula. Recently, the GCC have stated this:
We expect students to be taught evidence-based practice: integrating individual clinical expertise, the best available evidence from current and credible clinical research, and the values and preferences of patients. Chiropractors are important members of a patient’s healthcare team, and interprofessional approaches enable the best outcomes. Programmes that meet these Standards will teach ethical, professional care and produce competent healthcare professionals who can serve the needs of patients.
These are indeed most encouraging words!
Basically, they are saying that chiropractic education will now have to be solidly based on the principles of evidence-based medicine (EBM) as well as sound medical ethics. Let me spell out what this really means. Chiropractic courses must teach that:
- The current and credible clinical evidence suggesting that spinal manipulations, the hallmark intervention of chiropractors, are effective is weak for back pain and negative or absent for all other conditions.
- The current and credible clinical evidence suggests that spinal manipulations, the hallmark intervention of chiropractors, can cause harm which in many instances is serious.
- The current and credible clinical evidence thus suggests that the risk/benefit balance for spinal manipulations, the hallmark intervention of chiropractors, is not positive.
- Medical ethics require that competent healthcare professionals inform their patients that spinal manipulations, the hallmark intervention of chiropractors, may not generate more good than harm which is the reason why they cannot employ these therapies.
So, the end of chiropractic in the UK is looming!
Unless, of course, the GCC’s words are not really meant to be translated into action. They could be just window dressing and politically correct bullshit. But that’ s really far too far fetched – after all they come from the GENERAL CHIROPRACTIC COUNCIL, known for its excellent track record, e.g.:
- The GCC “seems to be a little self-regulatory chiropractic bubble where chiropractors regulate chiropractors.”
- A 5-year strategy for UK chiropractors: not fit for purpose
- Chiro behaving badly… is the GCC fit for purpose?
- The UK General Chiropractic Council: fit for purpose?
- Farcical Chiropractic Council: Chiropractic Patient Satisfaction and Experience
- The General Chiropractic Council “regulates chiropractors to ensure the safety of patients” … well, you could have fooled me!
- Death of a chiropractic patient prompts a reaction by the UK General Chiropractic Council
According to chiropractic belief, vertebral subluxation (VS) is a clinical entity defined as a misalignment of the spine affecting biomechanical and neurological function. The identification and correction of VS is the primary focus of the chiropractic profession. The purpose of this study was to estimate VS prevalence using a sample of individuals presenting for chiropractic care and explore the preventative public health implications of VS through the promotion of overall health and function.
A brief review of the literature was conducted to support an operational definition for VS that incorporated neurologic and kinesiologic exam components. A retrospective, quantitative analysis of a multi-clinic dataset was then performed using this operational definition.
The operational definition used in this study included:
- (1) inflammation of the C2 (second cervical vertebra) DRG,
- (2) leg length inequality,
- (3) tautness of the erector spinae muscles,
- (4) upper extremity muscle weakness,
- (5) Fakuda Step test,
- radiographic analysis based on the (6) frontal atlas cranium line and (7) horizontal atlas cranium line.
Descriptive statistics on patient demographic data included age, gender, and past health history characteristics. In addition to calculating estimates of the overall prevalence of VS, age- and gender-stratified estimates in the different clinics were calculated to allow for potential variations.
A total of 1,851 patient records from seven chiropractic clinics in four states were obtained. The mean age of patients was 43.48 (SD = 16.8, range = 18-91 years). There were more females (n = 927, 64.6%) than males who presented for chiropractic care. Patients reported various reasons for seeking chiropractic care, including, spinal or extremity pain, numbness, or tingling; headaches; ear, nose, and throat-related issues; or visceral issues. Mental health concerns, neurocognitive issues, and concerns about general health were also noted as reasons for care. The overall prevalence of VS was 78.55% (95% CI = 76.68-80.42). Female and male prevalence of VS was 77.17% and 80.15%, respectively; notably, all per-clinic, age, or gender-stratified prevalences were ≥50%.
The authors concluded that the results of this study suggest a high rate of prevalence of VS in a sample of individuals who sought chiropractic care. Concerns about general health and wellness were represented in the sample and suggest chiropractic may serve a primary prevention function in the absence of disease or injury. Further investigation into the epidemiology of VS and its role in health promotion and prevention is recommended.
This is one of the most hilarious pieces of ‘research’ that I have recently encountered. The strategy is siarmingly simple:
- invent a ficticious pathology (VS) that will earn you plently of money;
- develop criteria that allow you to diagnose this pathology in the maximum amount of consumers;
- show gullible consumers that they are afflicted by this pathology;
- use scare mongering tactics to convince consumers that the pathology needs treating;
- offer a treatment that, after a series of expensive sessions, will address the pathology;
- cash in regularly while this goes on;
- when the consumer has paid enough, declare that your fabulous treatment has done the trick and the consumer is again healthy.
The strategy is well known amongst practitioners of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM), e.g.:
- Traditional acupuncturists diagnose a ficticious imbalance of yin and yang only to normalise it with numerous acupuncture sessions.
- Naturopaths diagnose ficticious intoxications and treat it with various detox measures.
- Iridologists diagnose ficticious abnormalities of the iris that allegedly indicate organ disstress and treat it with whatever SCAM they can offer.
As they say:
No disease can be more surely, effectively, and profitably treated than a condition that the unsuspecting customer did not have in the first place!
PS
Sadly, such behavior exists in convertional medicine occasionally too, but SCAM relies almost entirely on it.
I was alerted to a new book entitled “Handbook of Space Pharmaceuticals“. It contains a chapter on “Homeopathy as a Therapeutic Option in Space” (yes, I am not kidding!). Here is its abstract (the numbers were inserted by me and refer to the short comments below):
Homeopathy is one of the largest used unorthodox medicinal systems having a wide number of principles and logic to treat and cure various diseases [1]. Many successful concepts like severe dilution to high agitation have been applied in the homeopathic system [2]. Though many concepts like different treatment for same diseases and many more are contradictory to the allopathic system [3], homeopathy has proved its worth in decreasing drug-related side effects in many arenas [4]. Various treatments and researches are carried out on various diseases; mostly homeopathic treatment is used in joint diseases, respiratory diseases, cancer, and gastrointestinal tract diseases [5]. In this chapter, readers will have a brief idea about many meta-analysis results of most common respiratory diseases, i.e., asthma, incurable hypertension condition, rheumatoid arthritis, and diarrhea and a megareview of all the diseases to see their unwanted effects, uses of drugs, concepts, and issues related to homeopathy [6]. Various limitations of homeopathic treatments are also highlighted which can give a clear idea about the future scope of research [7]. Overall, it can be concluded that placebo and homeopathic treatments give almost the same effect [8], but the less severe side effects of homeopathic drugs in comparison to all other treatment groups catch great attention [9].
Apart from the very poor English of the text and the fact that it has as good as nothing to do with the subject of ‘Homeopathy as a Therapeutic Option in Space’, I have the following brief comments:
- I did not know that homeopathy has ‘a wide number of logic’ and had alwas assumed that there is only one logic.
- Successful concepts? Really?
- So, homeopaths believe that the ‘allopathic system’ treats the same diseases uniformly? In this case, they should perhaps read up what conventional medicine really does.
- I am not aware of good evidence showing that homeopathy reduces drug related adverse effects.
- No, homeopathy is used for all symptoms – Hahnemann did not believe in treating disease entities – and mostly for those that are self-limiting.
- I love the term ‘incurable hypertension condition’; can somebody please explain what it is?
- The main limitation is that homeopathy is nonsense and, as such, does not really require further research.
- Not ‘almost’ but ‘exactly’! But thanks for pointing it out.
- Wishful thinking and not true. Firstly, the author forgot about ‘homeopathic aggravations’ in which homeopaths so strongly believe. Secondly, I know of many non-homeopathic treatments that are free of adverse effects when done properly.
Altogether, I am as disappointed by this article as you must be: we were probably all hoping to hear about the discovery showing that homeopathy works splendidly in space – not least because we have known for a while that homeopaths seem to be from a different planet.
On the occasion of a talk that I recently gave in Italy, I was interviewed by VANITY FAIR ITALY. I gave it in English and it was published in Italian. As I don’t expect many readers to be fluent in Italian and since it was a good interview, in my view, I thought I give you here the English original:
1.How can we exactly define «alternative medicine»?
There is much confusion and a plethora of definitions, none of which is fully satisfactory. In fact, the term “alternative medicine” itself is nonsensical: if a therapy works, it belongs to evidence-based medicine; and if it doesn’t work, it cannot possibly be an alternative. I therefore have long been calling it “so-called alternative medicine” (SCAM). The definition I use for SCAM with lay audiences is simple: SCAM is an umbrella term for a diverse range of therapeutic and diagnostic methods that have little in common, other than being excluded from mainstream medicine.
2.Who uses it and why?
Predominantly women! Statistics say about 30-70% of the general population use SCAM. And with patient populations, the percentage can be close to 100%. They use it because they are told over and over again that SCAM is natural and thus safe, as well as effective for all sorts of conditions.
3.Focusing on terminology, is there a difference between «complementary» and «alternative» medicine?
Theoretically, there is a big difference between «complementary» and «alternative» medicine. The former is supposed to be used as an add-on to, while the latter is a replacement of mainstream medicine. In practice, this dividing line is very blurred; most SCAMs are used in both ways, depending on the actual situation and circumstance.
4.Are users different from non-users?
Yes, there has been much research on this and my reading of it is that SCAM users tend to be less intelligent, more religious, more superstitious, less trusting in science, and more prone to conspiracy theories, for instance.
5.Which forms of alternative medicine are the most popular?
There are certain national differences, but in most European countries herbal medicine, acupuncture, chiropractic, osteopathy, homeopathy, aromatherapy, and reflexology are amongst the most popular SCAMs.
6.Does it work?
With such a wide range – someone once counted over 400 modalities and my last book evaluated 202 of them (Alternative Medicine: A Critical Assessment of 202 Modalities (Copernicus Books): Amazon.co.uk: Ernst, Edzard: 9783031107092: Books) – it is impossible to answer with yes or no. In addition we need to consider the conditions that are being treated. Acupuncture, for example, is touted as a panacea, but might just work for pain. If you take all this into account, I estimate that less than 3% of the therapeutic claims that are being made for SCAM are supported by sound evidence.
Is it safe?
Again, impossible to say. Some treatments are outright dangerous; for instance, chiropractic neck manipulations can injure an artery and the patient suffers a stroke of which she can even die. Other treatments are assumed to be entirely harmless; for example homeopathy. But even that is untrue: if a cancer patient relies exclusively on homeopathy for a cure, she might easily hasten her death. Sadly, such things happen not even rarely.
Do its benefits outweigh its risks?
That depends very much on the treatment, the disease, and the precise situation. Generally speaking, there are very few SCAMs that fulfill this condition.
You said that these were the research questions that occupied all your life in Exeter. Did you find the answers?
We published more on SCAM than any other research group, and we found mostly disappointing answers. But still, I am proud of having found at least some of the most pressing answers. Even negative answers can make an important contribution to our knowledge.
7.What is the problem with the placebo effect?
All therapies can prompt a placebo effect. Thus an ineffective treatment can easily appear to be effective through generating a placebo effect. This is why we need to rely on properly conducted, if possible placebo-controlled trials, if we want to know what works and what not.
8.Is it true that some alternative medicines can cause significant harm?
see above
9.What about herbal remedies? What do studies show about them?
Many of our modern drugs originate from plants, Therefore, it is not surprising that we find herbal remedies that are effective. But careful! This also means that plants can kill you – think of hemlock, for instance. In addition herbal medicine can interact powerfully with synthetic drugs. So, it is wise to be cautious and get responsible advice.
10.Which alternative therapies are overrated and why?
In my view, almost all SCAMs are over-rated. If you go on the Internet, you find ~5 000 000 websites on SCAM. 99% of them try to sell you something and are unreliable or even dangerous. We need to be aware of the fact that SCAM has grown into a huge business and many entrepreneurs are out to get your money based on bogus claims.
11.On the contrary, which therapies could be seen as an integration in routine care?
The best evidence can be found in the realm of herbal medicine, for instance St John’s Wort. Some mind-body interventions can be helpful; also a few massage techniques might be worth a try. Not a lot, I’m afraid.
12.Would you tell us what happened in 2005 with Prince Charles?
He complained about my actions via his private secretary to my University. A 13 month investigation followed. At the end, I was found not guilty but my funding, my team, my infrastructure had been dismantled. So, in effect, Charles managed to close down what was the only research group that looked critically and systematically into SCAM. A sad story – not so much for me but for progress and science, I think.
3.Why is alternative medicine still a controversial subject?
Mainly because the gap between the claims and the evidence is so very wide – and getting wider all the time.
14.Would you suggest the «right way» to approach it?
I often recommend this: if it sounds too good to be true, it probably is! I might add that, if you want reliable advice, don’t listen to those who profit from giving it.
We have often discussed cupping on this blog, e.g.:
- The ‘WORST PAPER OF 2022 COMPETITION’ entry No 6: “The efficacy and safety of dry cupping in cervical spondylosis with optimization of cup application time – A randomized clinical trial”
- Cupping therapy for non-specific chronic low back pain
- Cupping for Olympic swimmers. Or: why breaking your shoulder is not necessarily good for writing a successful book
- Infant receiving cupping treatment prompts outrage
Yes, generally speaking I have been critical about cupping – not because I don’t like it (I even used the treatment as a young clinician many years ago) but because the evidence tells me to. I was glad to see that the authors of a recent article entitled “Utility of Cupping Therapy in Substance Use Disorder: A Novel Approach or a Bizarre Treatment?” offer even more outspoken words about the therapy. Here are their conclusions:
Established treatment modalities for substance use disorder and its withdrawal symptoms include pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy, but their utilization by the general population remains unsatisfactory. Taboos regarding mental health services and concerns about confidentiality are massive obstacles for patients seeking psychiatric help, and alternative forms of medicine may seem more approachable, even with the associated risks. As displayed in this case, cupping therapy is a traditional therapy with no role in treating polyaddiction and withdrawal symptoms, but it unnecessarily exposes individuals to really uncomfortable and often concealed complications such as bruising, and skin and blood infections, especially when carried out by untrained, incompetent individuals. While one can explore these options in addition to seeking professional mental health care, it is imperative to spread awareness about the roles, scientific soundness, and adverse effects of these alternative health practices. The health promotion and education sectors need reforms to educate the general population, especially the rural population in India, about the dangers of iatrogenesis caused by non-evidence-backed treatments. There needs to be an extensive advertisement of only the most effective and scientific treatment options provided by medical professionals, and the risks of overlooking them in favor of traditional cures propagated by unqualified individuals. With all the scientific advancements in the 21st century ranging from artificial intelligence in healthcare, and robotic surgeries, to extensive clinical trials for novel anti-cancer drugs, we cannot allow the propagation of ancient, scientifically unsound techniques that may cause more harm than benefit to patients.
Why, I am sure you ask yourself, are they so critical? The reason lies in the case they report in the same paper:
A 30-year-old man presented to the psychiatric outpatient department with complaints of nervousness, anxiety, a sense of impending doom, irritability, anger outbursts, headache, and reduced sleep and appetite for the last five days. The patient had a history of daily consumption of 5-10 mg of alprazolam tablets, 200-250 mg of codeine syrup, and about five packets of chewable tobacco over the last seven years; this was a pattern of polyaddiction to a benzodiazepine, opiate, and nicotine. The patient had no history of fever, confusion, or hallucinations. On eliciting the past history, the patient revealed that he went to an alternative medicine practitioner after his family persuaded him to seek help for his substance use disorder. After ceasing the consumption of all three substances for three days, he started developing the symptoms with which he presented to our hospital. He was hesitant to talk about his substance use disorder to medical professionals and concerned about confidentiality, and, hence, went to an alternative medicine practitioner whom he deemed approachable. There he was given wet cupping therapy on the head for four days, which involved the use of rubber pumps to create a suction inside the cups placed on his head. After three to five minutes, the cups were removed and small incisions were made on the cupping sites, following which a second suction caused the oozing out of blood from the incision sites on the scalp (Figure 1). But, this did not improve his symptoms, and hence, he stopped going there two days before coming to our tertiary care hospital.
On examination, the patient had a pulse rate of 76 beats per minute, blood pressure of 128/78 mm Hg, and respiratory rate of 22 per minute. He was well-oriented to time, place, and person. Systemic examination of the cardiovascular system was unremarkable. He denied any other substance use. The skin over his head had distinct cupping marks but no signs of infection or active bleeding, which are some common complications after cupping therapy (Figure 2). On assessment, the patient had a Clinical Opiate Withdrawal Scale (COWS) score of 13 and a Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment (CIWA) scale score of 26.
Later, the patient was admitted to the psychiatric ward to manage the withdrawal symptoms, where we initiated pharmacotherapy. Tablet diazepam (20 mg/day), sodium valproate (800 mg/day), tramadol (200 mg/day), thiamine (300 mg/day), paracetamol (500 mg/day) and intravenous fluids were given to the patient. We counseled the patient regarding substance abuse, its harmful effects, and de-addiction. The patient’s symptoms started to improve, and we continued the treatment for four days and discharged him with a COWS score of 4 and a CIWA score of 2. We intended to reassess him after 14 days, but we lost him to follow-up.
We have repeatedly discussed the fraud committed by many chiropractors. A recent article provided further information on this lamentable issue. Here are a few excerpts:
Fraud in US chiropractic care is on the rise. A shocking 82 percent of the chiropractic services billed to Medicare is unallowable, according to a recent audit by the Office of Inspector General. The audit found a lack of effective controls allowed an estimated $358.8 million in taxpayer funds to be improperly billed to Medicare.
Chiropractors engage in fraudulent billing practices in a variety of ways. Sometimes they target environments like nursing homes or substance abuse rehabilitation centers, looking for new patients who may – or may not – require their services.
In one case, a St. Louis-based chiropractor bribed police officers to get access to personal information about individuals who had been in car accidents. The chiropractor then contacted the accident victims and claimed to be from an insurance company or the state to arrange appointments at his practice.
In another case, a Houston-based chiropractor and his medical group settled with the federal government for $2.6 million and were also banned from billing federal programs for 10 years due to their involvement with a fraudulent billing scheme.
Lastly, in 2021, a chiropractor was found guilty of federal criminal charges, including five counts of healthcare fraud. The chiropractor was accused of defrauding health insurers by submitting $2.2 million in billings for chiropractic services that were never provided, office visits that never occurred, false diagnoses, and falsely prescribed medical devices.
Although other medical specialties also have bad actors, certain specific reasons can be identified as to why fraudulent billing and abuse have been increasing among chiropractors. These practitioners have fewer lower-cost codes to bill for, which means they need more patients to boost their earnings. For example, a service may only be billed at $25 or $50, but if this is billed to every patient on every visit, it quickly adds up. Because employers often have limited resources, it’s easy for minor charges to go unnoticed.
According to a 2018 report, the inspector general has conducted numerous evaluations and audits of chiropractic services since 2005 and has identified hundreds of millions of dollars in overpayments for services that did not meet Medicare requirements. The report also noted that the OIG’s investigations and legal actions involving chiropractors have demonstrated that chiropractic services are susceptible to healthcare fraud.
______________
Personally, I am not surprised by such reports. Sure, not all chiropractors committ financial fraud. But arguably ALL chiropractors are dishonest when they tell their patients that their spinal manipulations are effective and safe for a wide range of conditions. To put it bluntly: chiropractic was founded by a crook on a bunch of lies and unethical behavior, therefore, it is hardly surprising that today the profession has a problem with honesty and fraudulent behavior.


