Monthly Archives: October 2022
We have repeatedly discussed the issue of detox as used in so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) and seen that, for a whole range of reasons, it is utter nonsense, e.g.:
- Remember Prince Charles’ ‘Duchy Originals Detox Tincture’?
- Now that you have paid through your nose for the ‘tox’, how about a ‘detox’ through your nose?
- Homotoxicology: ‘the best kept detox secret’? No, it’s even worse than homeopathy!
- Detox is bunk; save your money for something useful, fun or pleasant!
- Scientology detox? No thanks!!!
- ‘DETOX’ = a dangerous and counter-productive illusion
- Have yourself a merry little detox
- It’s beginning to look a lot like DETOX…everywhere I go
But would it not be better to keep toxins from entering the body in the first place?
Yes, you suspected correctly: there are products that claim to do exactly this. Here is a particularly ‘impressive’ one:
ION* Gut Support seals cells in the gut lining, helping to keep toxins out of your body and strengthening the terrain upon which your microbiome can diversify. it uses Humic Extract (from Ancient Soil) and Purified Water.
Humic extract is sourced from ancient soil (roughly 60 million years old), and contains a blend of bacterial metabolites (aka, fulvate) as well as less than 1% of a variety of trace minerals and amino acids including chloride, sodium, lithium, calcium, phosphorus, sulfur, bromide, potassium, iron, antimony, zinc, copper, gold, magnesium, alanine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine, and valine.
… the trace minerals in our humic extract are naturally occurring, well below the RDI, and not meant to be used as supplementary to any deficiencies. The truly active compound in humic extract is the fulvate, a unique family of carbon molecules with oxygen-binding sites that are produced by bacteria when they digest nutrients. These molecules are the backbone of the ION* blend, helping with critical functions like cellular and microbial communication and chelation of nutrients.
The science behind ION* lies in strengthening the cellular integrity of your body’s barriers, including not just your gut, but your sinuses and skin as well. Keeping your cells connected keeps these barriers intact, which sets the stage (or “terrain” as we like to call it) for seamless interaction between you and your microbiome.
At ION*, we’re all about connection – starting with the very foundation of our science: tight junction integrity. Tight junctions are the seals between your cells which help to create defensive barriers at the gut, skin, and sinuses. They act intelligently to keep toxins and foreign particles out of the blood stream while also allowing nutrients to enter. These seals are protected by the carbon and mineral metabolites of bacterial digestion.
Unfortunately, tight junction barriers can be degraded with exposure to gluten, glyphosate (the main chemical in commercial herbicides like Roundup), and other environmental insults. ION* has been scientifically shown to promote the strengthening of this barrier through redox signaling, even in the face of those environmental insults.
Your body’s barriers know what to let in (nutrients) and what to ward off (toxins). But the barriers must be strong. ION* works to strengthen your gut, sinus, and skin barriers at a cellular level by fostering tight junction integrity, helping to promote this intelligent defense system at a foundational level.
So much scientific-sounding language can make your head spin.
Which toxins are we talking about?
Are there any clinical studies of the product?
Why is the product so expensive?
What exactly are Humic substances?
I found an answer to only the last question. Humic substances are organic compounds that are important components of humus, the major organic fraction of soil, peat, and coal, and also a constituent of many upland streams, dystrophic lakes, and ocean water.
I imagine that tightening the named junctions – if this is truly a realistic mechanism of action – might interfere with the absorption of all sorts of substances that the body needs for survival. I am, of course, speculating, but one should ask about the risks of using this product (other than the one to the consumer’s bank account).
What we need are clinical studies. And there seem to be none (if anyone knows one, please let me know).
So, what do we call again a health product that makes unsubstantiated claims?
Was it perhaps ‘snake oil’?
It has been reported that a father accused of withholding insulin from his eight-year-old diabetic daughter and relying on the healing power of God has been committed to stand trial for her alleged murder.
Jason Richard Struhs, his wife Kerrie, and 12 others from a fringe religious group have been charged over the death of type 1 diabetic Elizabeth Rose Struhs. Police alleged she had gone days without insulin and then died. The police prosecutor detailed statements from witnesses and experts, including pediatric consultant Dr. Catherine Skellern, who said Elizabeth’s death “would have been painful and was over a prolonged period of days”.
“There is [also] body-worn camera footage at the scene … where Jason Struhs has recounted the events of the week leading up to the death of Elizabeth,” said the prosecutor. “This details the decision that Jason Struhs has made to stop the administration of insulin, and he stated that he knew the consequences, and he stated in that recording that he will ‘probably go to jail like they put Kerrie in jail’.”
 During the hearing, Struhs, who appeared from jail by videolink, mainly sat with his head bowed and hands clasped against his forehead as magistrate Clare Kelly described the evidence against him. “It is said that Mr. Struhs, his wife Kerrie Struhs, and their children, including Elizabeth, were members of a religious community… The religious beliefs held by the members of the community include the healing power of God and the shunning of medical intervention in human life.” She also described a statement from Skellern suggesting Elizabeth would have spent her final days suffering from “insatiable thirst, weakness and lethargy, abdominal pain, incontinence, and the onset of impaired levels of consciousness”. The evidence read into court was an attempt by prosecutors to firm up an additional charge of torture. She said a post-mortem found Elizabeth’s cause of death was diabetic ketoacidosis, caused by a lack of insulin. “It is a life-threatening condition, which requires urgent medical treatment,” Kelly said.
During the hearing, Struhs, who appeared from jail by videolink, mainly sat with his head bowed and hands clasped against his forehead as magistrate Clare Kelly described the evidence against him. “It is said that Mr. Struhs, his wife Kerrie Struhs, and their children, including Elizabeth, were members of a religious community… The religious beliefs held by the members of the community include the healing power of God and the shunning of medical intervention in human life.” She also described a statement from Skellern suggesting Elizabeth would have spent her final days suffering from “insatiable thirst, weakness and lethargy, abdominal pain, incontinence, and the onset of impaired levels of consciousness”. The evidence read into court was an attempt by prosecutors to firm up an additional charge of torture. She said a post-mortem found Elizabeth’s cause of death was diabetic ketoacidosis, caused by a lack of insulin. “It is a life-threatening condition, which requires urgent medical treatment,” Kelly said.
___________________________
Cases like these are tragic, all the more so because they might have been preventable with more information and critical thinking. They make me desperately sad, of course, but they also convince me that my work with this blog should continue.
Osteopathy is becoming under increasing criticism – not just in the UK but also in other countries. Here are the summary points from a very good overview from Canada:
– Osteopathy is based on the belief that illness comes from the impaired movement of muscles, bones, and their connecting structures, and that an osteopath can restore proper movement using their hands
– Offshoots of osteopathy include visceral osteopathy and craniosacral osteopathy, which make extraordinary claims that are not backed up by good evidence
– There is an absence of good quality evidence to support the use of osteopathy to address musculoskeletal issues
– Osteopathy has been reformed in the United States, with osteopathic physicians receiving training comparable to medical doctors and few of them regularly using osteopathic manual manipulations
An article from Germany is equally skeptical. Here is my translation of an excerpt from a recent article:
When asked which studies prove the effectiveness, the VOD kindly and convincingly handed the author of this article a list of about 20 studies. And emphasized that these were listed in Medline, i.e. a recognized medical database. But a close examination of the studies reveals: Almost without exception, all of them qualify their results and point to uncertainties.
The treatment is “possibly helpful,” for example, they say, the study quality is “very low,” “low” to “moderate,” there are too few studies, they are small, the “evidence is preliminary” and “insufficient to draw definitive conclusions. Again and again it is emphasized that further, methodically better, more sustainable studies are needed, which also record more precisely what happened in osteopathic treatment in the first place.
Another article was published by myself in ‘L’Express’. As it is in French, I translated the conclusion for you:
… would I recommend consulting an osteopath? My answer is a carefully considered NO! For patients with back pain, the evidence is as good (or bad, depending on your point of view) as for many other proposed therapies. So if a patient insists on osteopathy, I might support it, but I would still prefer physical therapy. For all other musculoskeletal conditions, there is not enough evidence to make positive recommendations. For patients with conditions other than musculoskeletal, I would advise against osteopathy.
All this comes after it has been shown that worldwide research into osteopathy is scarce and has hardly any impact at all. The question we should therefore ask is this:
why do we need osteopaths?
PS
Osteopaths in the US have studied medicine, rarely practice manual treatments, and are almost indistinguishable from MDs. Everywhere else, osteopaths are practitioners of so-called alternative medicine.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of acupuncture on cognitive task performance in college students.
Sixty students aged 18-25 years were randomly allocated into acupuncture group (AG) (n=30) and control group (CG) (n=30). The AG underwent 20 min of acupuncture/day, while the CG underwent their normal routine for 10 days. Assessments were performed before and after the intervention.
Between-group analysis showed a significant increase in AG’s six-letter cancellation test (SLCT) score compared with CG. Within-group analysis showed a significant increase in the scores of all tests (i.e. SLCT, forward and backward Digit span test [DST]) in AG, while a significant increase in backward DST was observed in CG.
The authors concluded that acupuncture has a beneficial effect on improving the cognitive function of college students.
I am unable to access the full paper [it is behind a paywall]. Thus, I am unable to assess the study in further detail. As I am skeptical about the validity of the effect, I can only assume that it is due to the expectation of the volunteers receiving acupuncture. There was not even an attempt to control for placebo effects!
The over-stated conclusion made me wonder what else the 1st author has published. It turns out he has three more Medline-listed papers to his name all of which are about so-called alternative medicine (SCAM).
The 1st one is an RCT similar to the one above, i.e. without an attempt to control for placebo effects. Its conclusion is equally over-stated: Acupuncture could be considered as an effective treatment modality for the management of primary dysmenorrhea.
The other two papers refer to one case report each. Despite the fact that case reports (as any researcher must know) do not lend themselves to conclusions about the effectiveness of the treatments employed, the authors’ conclusions seem to again over-state the case:
- This suggests that integrative Naturopathy and Yoga therapies could be considered as an adjuvant to conventional medicine in rheumatoid arthritis associated with type-2 diabetes and essential hypertension.
- Though the results are encouraging, further studies are required with larger sample size and advanced inflammatory markers.
What does that tell us?
I don’t know about you, but I would not rely on acupuncture to improve my mental performance.
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are highly prevalent, burdensome, and putatively associated with an altered human resting muscle tone (HRMT). Osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) is commonly and effectively applied to treat MSDs and reputedly influences the HRMT. Arguably, OMT may modulate alterations in HRMT underlying MSDs. However, there is sparse evidence even for the effect of OMT on HRMT in healthy subjects.
A 3 × 3 factorial randomized trial was performed to investigate the effect of myofascial release (MRT), muscle energy (MET), and soft tissue techniques (STT) on the HRMT of the corrugator supercilii (CS), superficial masseter (SM), and upper trapezius muscles (UT) in healthy subjects in Hamburg, Germany. Participants were randomised into three groups (1:1:1 allocation ratio) receiving treatment, according to different muscle-technique pairings, over the course of three sessions with one-week washout periods. We assessed the effect of osteopathic techniques on muscle tone (F), biomechanical (S, D), and viscoelastic properties (R, C) from baseline to follow-up (primary objective) and tested if specific muscle-technique pairs modulate the effect pre- to post-intervention (secondary objective) using the MyotonPRO (at rest). Ancillary, we investigate if these putative effects may differ between the sexes. Data were analysed using descriptive (mean, standard deviation, and quantiles) and inductive statistics (Bayesian ANOVA). 59 healthy participants were randomised into three groups and two subjects dropped out from one group (n = 20; n = 20; n = 19–2). The CS produced frequent measurement errors and was excluded from analysis. OMT significantly changed F (−0.163 [0.060]; p = 0.008), S (−3.060 [1.563]; p = 0.048), R (0.594 [0.141]; p < 0.001), and C (0.038 [0.017]; p = 0.028) but not D (0.011 [0.017]; p = 0.527). The effect was not significantly modulated by muscle-technique pairings (p > 0.05). Subgroup analysis revealed a significant sex-specific difference for F from baseline to follow-up. No adverse events were reported.
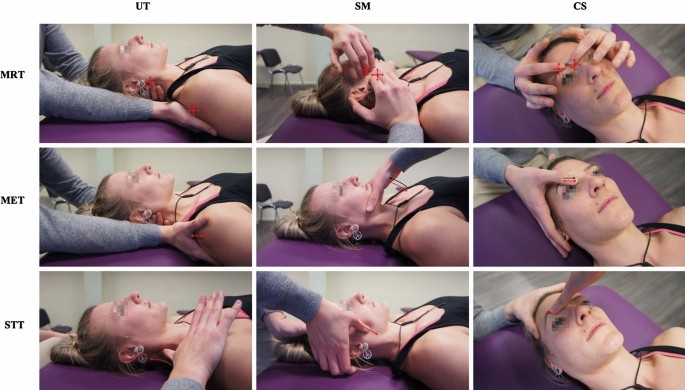
The authors concluded that OMT modified the HRMT in healthy subjects which may inform future research on MSDs. In detail, MRT, MET, and STT reduced the muscle tone (F), decreased biomechanical (S not D), and increased viscoelastic properties (R and C) of the SM and UT (CS was not measurable). However, the effect on HRMT was not modulated by muscle–technique interaction and showed sex-specific differences only for F.
I think that this study merits a few comments:
- It seems unsurprising that manual manipulation can relax muscles.
- The blinding of the volunteers was compromised because the participants were osteopathy students able to distinguish between the different interventions.
- The mechanisms underlying these reported changes in HRMT following OMT are unclear.
- The effects do not seem to be treatment-specific.
- The treatments used are not typical for osteopathy.
- Manual techniques are loosely defined or standardized.
- The duration of the effect is unknown but probably short.
- The size of the effect is small.
- The clinical relevance of the effect is doubtful.
Advocates of so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) often sound like a broken record to me. They bring up the same ‘arguments’ over and over again, no matter whether they happen to be defending acupuncture, energy healing, homeopathy, or any other form of SCAM. Here are some of the most popular of these generic ‘arguments’:
1. It helped me
The supporters of SCAM regularly cite their own good experiences with their particular form of treatment and think that this is proof enough. However, they forget that any symptomatic improvement they may have felt can be the result of several factors that are unrelated to the SCAM in question. To mention just a few:
- Placebo
- Regression towards the mean
- Natural history of the disease
2. My SCAM is without risk
Since homeopathic remedies, for instance, are highly diluted, it makes sense to assume that they cannot cause side effects. Several other forms of SCAM are equally unlikely to cause adverse effects. So, the notion is seemingly correct. However, this ‘argument’ ignores the fact that it is not the therapy itself that can pose a risk, but the SCAM practitioner. For example, it is well documented – and, on this blog, we have discussed it often – that many of them advise against vaccination, which can undoubtedly cause serious harm.
3. SCAM has stood the test of time
It is true that many SCAMs have survived for hundreds or even thousands of years. It is also true that millions still use it even today. This, according to enthusiasts, is sufficient proof of SCAM’s efficacy. But they forget that many therapies have survived for centuries, only to be proved useless in the end. Just think of bloodletting or mercury preparations from past times.
4 The evidence is not nearly as negative as skeptics pretend
Yes, there are plenty of positive studies on some SCAMs This is not surprising. Firstly, from a purely statistical point of view, if we have, for instance, 1 000 studies of a particular SCAM, it is to be expected that, at the 5% level of statistical significance, about 50 of them will produce a significantly positive result. Secondly, this number becomes considerably larger if we factor in the fact that most of the studies are methodologically poor and were conducted by SCAM enthusiasts with a corresponding bias (see my ALTERNATIVE MEDICINE HALL OF FAME on this blog). However, if we base our judgment on the totality of the most robust studies, the bottom line is almost invariably that there is no overall convincingly positive result.
5. The pharmaceutical industry is suppressing SCAM
SCAM is said to be so amazingly effective that the pharmaceutical industry would simply go bust if this fact became common knowledge. Therefore Big Pharma is using its considerable resources to destroy SCAM. This argument is fallacious because:
- there is no evidence to support it,
- far from opposing SCAM, the pharmaceutical industry is heavily involved in SCAM (for example, by manufacturing homeopathic remedies, dietary supplements, etc.)
6 SCAM could save a lot of money
It is true that SCAMs are on average much cheaper than conventional medicines. However, one must also bear in mind that price alone can never be the decisive factor. We also need to consider other issues such as the risk/benefit balance. And a reduction in healthcare costs can never be achieved by ineffective therapies. Without effectiveness, there can be no cost-effectiveness.
7 Many conventional medicines are also not evidence-based
Sure, there are some treatments in conventional medicine that are not solidly supported by evidence. So why do we insist on solid evidence for SCAM? The answer is simple: in all areas of healthcare, intensive work is going on aimed at filling the gaps and improving the situation. As soon as a significant deficit is identified, studies are initiated to establish a reliable basis. Depending on the results, appropriate measures are eventually taken. In the case of negative findings, the appropriate measure is to exclude treatments from routine healthcare, regardless of whether the treatment in question is conventional or alternative. In other words, this is work in progress. SCAM enthusiasts should ask themselves how many treatments they have discarded so far. The answer, I think, is zero.
8 SCAM cannot be forced into the straitjacket of a clinical trial
This ‘argument’ surprisingly popular. It supposes that SCAM is so individualized, holistic, subtle, etc., that it defies science. The ‘argument’ is false, and SCAM advocates know it, not least because they regularly and enthusiastically cite those scientific papers that seemingly support their pet therapy.
9 SCAM is holistic
This may or may not be true, but the claim of holism is not a monopoly of SCAM. All good medicine is holistic, and in order to care for our patients holistically, we certainly do not need SCAM.
1o SCAM complements conventional medicine
This argument might be true: SCAM is often used as an adjunct to conventional treatments. Yet, there is no good reason why a complementary treatment should not be shown to be worth the effort and expense to add it to another therapy. If, for instance, you pay for an upgrade on a flight, you also want to make sure that it is worth the extra expenditure.
11 In Switzerland it works, too
That’s right, in Switzerland, a small range of SCAMs was included in basic health care by referendum. However, it has been reported that the consequences of this decision are far from positive. It brought no discernible benefit and only caused very considerable costs.
I am sure there are many more such ‘arguments’. Feel free to post your favorites!
My point here is this:
the ‘arguments’ used in defense of SCAM are not truly arguments; they are fallacies, misunderstandings, and sometimes even outright lies.
The ‘Münster Circle‘ is an informal association of multi-disciplinary experts who critically examine issues in and around so-called alternative medicine (SCAM). We exist since June 2016 and are the result of an initiative by Dr Bettina Schöne-Seifert, Professor and Chair of Professor and Chair of Medical Ethics at the University of Münster.
In the past, we have published several documents which have stimulated discussions on SCAM-related subjects. Yesterday, we have published our ‘MEMORANDUM INTEGRATIVE MEDICINE‘. It is a critical analysis of this subject and will hopefully make some waves in Germany and beyond.
Here is its English summary:
The merging of alternative medicine and conventional medicine has been increasingly referred to as Integrative (or Integrated) Medicine (IM) since the 1990s and has largely replaced other terms in this field. Today, IM is represented at all levels.
IM is often characterised with the thesis of the ‘best of both worlds’. However, there is no generally accepted definition of IM. Common descriptions of IM emphasise:
– the combination of conventional and complementary methods,
– the holistic understanding of medicine,
– the great importance of the doctor-patient relationship,
– the hope for optimal therapeutic success,
– the focus on the patient,
– the high value of experiential knowledge.
On closer inspection, the descriptions of IM show numerous inconsistencies. For example, medicine in the hands of doctors is stressed, but it is also emphasised that all relevant professions would be involved. Scientific evidence is emphasised, but at the same time, it is stressed that IM itself includes homeopathy as well as other unsubstantiated treatments and is only ‘guided’ by evidence, i.e. not really evidence-based. It is claimed that IM is to be understood as ‘complementary to science-based medicine’; however, this implies that IM itself is not science-based.
The ‘best of both worlds’ thesis impresses many. However, if one investigates what is meant by ‘best’, one finds that this term is not interpreted in nearly the same way as in conventional medicine. Many claims of IM are elementary components of all good medicine and thus cannot be counted among the characterising features of IM. Finally, it is hard to ignore the fact that the supporters of IM use it as a pretext to introduce unproven or disproven modalities into conventional medicine. Contrary to promises, IM has no discernible potential to improve medicine; rather, it creates confusion and entails considerable dangers. This cannot be in the interest of patients.
Against this background, it must be demanded that IM is critically scrutinised at all levels.
________________________
The present study was conducted to evaluate the effect of date palm on the sexual function of infertile couples. It was designed as a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted on infertile women and their husbands who referred to infertility clinics in Iran in 2019.
The intervention group was given a palm date capsule and the control group was given a placebo. Data were collected through female sexual function index and International Index of Erectile Function.
The total score of sexual function of females in the intervention group increased significantly from 21.06 ± 2.58 to 27.31 ± 2.59 (P < 0.0001). Also, other areas of sexual function in females (arousal, orgasm, lubrication, pain during intercourse, satisfaction) in the intervention group showed a significant increase compared to females in the control group, which was statistically significant (P < 0.0001).
All areas of male sexual function (erectile function, orgasmic function, sexual desire, intercourse satisfaction and overall satisfaction) significantly increased in the intervention group compared to the control group (P < 0.0001).
The authors concluded that the present study revealed that 1-month consumption of date palm has a positive impact on the sexual function of infertile couples.
In an attempt to explain the rational for this study, the authors state that, since ancient times, date palm has been used in Greece, China and Egypt to treat infertility and increase sexual desire and fertility in females. Rasekh indicated that Palm Pollen is effective in sperm parameters of infertile men. Administering date palm to male rats and measuring the sexual parameters of rats showed an improvement in their sexual function. Studies on animals have shown its effect on the parameters of semen analysis in male animals and increasing hormones.
So, the trial was what might call a ‘long shot’, even a very long one. But that does not render its findings less interesting. If the results could be confirmed, they would certainly have considerable significance.
But can they be confirmed?
I have some doubts.
Two things are remarkable, in my view.
- The study only had subjective endpoints.
- There was as good as no placebo effect in the control group.
How can this be?
One explanation might be that the verum and the placebo capsules were easily identified by their taste of other features. This would then lead to many patients being ‘deblinded’; in other words, the patients on verum would have known and expected to experience an effect, while the patients on placebo would have also known and be disappointed thus not even experiencing a placebo response.
This might be an apt reminder for trialists to include a check of the success of blinding in their list of outcome measures.
The problems for homeopathy in Germany do not seem to stop. Recently, the German health minister announced that he will look at the issue of reimbursement of homeopathy. Now, an article in the Deutsche Apotheker Zeitung (German Journal for Pharmacists) critically discussed the question of the place of homeopathy in German pharmacies. At present, pharmacies are the only places that are allowed to sell homeopathic preparations. This undoubtedly gives them a veneer of respectability; many consumers seem to feel that, if homeopathic preparations are only available in pharmacies, they must be well-tested and effective.
But recently, more and more German pharmacists have been pointing out that homeopathy is ineffective nonsense. A journalist who had listened to the advanced training “Homeopathy Highlights” of the Westphalia-Lippe Chamber of Pharmacists, he subsequently confronted the Chamber with the controversial contents of this advanced training event. The Chamber then declared that it would “no longer offer any refresher seminars on the subject of homeopathy with immediate effect” and that the speaker would also no longer work for it.
And now, the Berlin Chamber of Pharmacists wants the pharmacy community to distance itself from homeopathy as a scientifically recognized and evidence-based drug therapy. With its motion, the Chamber wants to achieve that the title “Naturopathic Medicine and Homeopathy” of the training regulations is replaced by the title “Phytopharmacy and Naturopathy”. The justification states: “The permission to use the title ‘pharmacist for naturopathic treatment and homeopathy’ by the state chambers of pharmacists suggests that homeopathy is a scientifically recognized and evidence-based drug therapy”.
I think it is time that German pharmacists remind themselves that they are more than shopkeepers; they are healthcare professionals who have an ethical duty. I have discussed this issue often enough. If you are interested, here are a few of my posts on this subject:
- Pharmacists must advise customers that homeopathic remedies lack evidence
- “Pharmacists should not sell or dispense homeopathic products”
- German pharmacists fail their customers when advising them on homeopathy
- Pharmacists put themselves at risk by selling homeopathic remedies
- Pro and Contra: should UK community pharmacists sell homeopathic remedies?
- Pharmacists’ responsibilities vis a vis alternative medicine: the violation of healthcare ethics continues.
- It is “disappointing that some pharmacists are still stocking homeopathy products”
- Pharmacists: to sell quackery means you are quacks – or have I got that wrong?
- Pharmacists must use their professional judgement to prevent the supply of homeopathic remedies
It is high time that German pharmacists do the right thing!
Bioenergy (or energy healing) therapies are among the popular alternative treatment options for many diseases, including cancer. Many studies deal with the advantages and disadvantages of bioenergy therapies as an addition to established treatments such as chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation in the treatment of cancer. However, a systematic overview of this evidence is thus far lacking. For this reason, German authors reviewed and critically examined the evidence to determine what benefits the treatments have for patients.
In June 2022, a systematic search was conducted searching five electronic databases (Embase, Cochrane, PsychInfo, CINAHL and Medline) to find studies concerning the use, effectiveness, and potential harm of bioenergy therapies including the following modalities:
- Reiki,
- Therapeutic Touch,
- Healing Touch,
- Polarity Therapy.
From all 2477 search results, 21 publications with a total of 1375 patients were included in this systematic review. The patients treated with bioenergy therapies were mainly diagnosed with breast cancer. The main outcomes measured were:
- anxiety,
- depression,
- mood,
- fatigue,
- quality of life (QoL),
- comfort,
- well-being,
- neurotoxicity,
- pain,
- nausea.
The studies were predominantly of moderate quality and, for the most part, found no effect. In terms of QoL, pain, and nausea, there were some positive short-term effects of the interventions, but no long-term differences were detectable. The risk of side effects from bioenergy therapies appears to be relatively small.
The authors concluded that considering the methodical limitations of the included studies, studies with high study quality could not find any difference between bioenergy therapies and active (placebo, massage, RRT, yoga, meditation, relaxation training, companionship, friendly visit) and passive control groups (usual care, resting, education). Only studies with a low study quality were able to show significant effects.
Energy healing is as popular as it is implausible. What these ‘healers’ call ‘energy’ is not how it is defined in physics. It is an undefined, imagined entity that exists only in the imagination of its proponents. So why should it have an effect on cancer or any other condition?
My team conducted 2 RCT of energy healing (pain and warts); both failed to show positive effects. And here is what I stated in my recent book about energy healing for any ailment:
Energy healing is an umbrella term for a range of paranormal healing practices. Their common denominator is the belief in a mystical ‘energy’ that can be used for therapeutic purposes.
- Forms of energy healing have existed in many ancient cultures. The ‘New Age’ movement has brought about a revival of these ideas, and today energy healing systems are amongst the most popular alternative therapies in the US as well as in many other countries. Popular forms of energy healing include those listed above. Each of these are discussed and referenced in separate chapters of this book.
- Energy healing relies on the esoteric belief in some form of ‘energy’ which is distinct from the concept of energy understood in physics and refers to some life force such as chi in Traditional Chinese Medicine, or prana in Ayurvedic medicine.
- Some proponents employ terminology from quantum physics and other ‘cutting-edge’ science to give their treatments a scientific flair which, upon closer scrutiny, turns out to be but a veneer of pseudo-science.
- The ‘energy’ that energy healers refer to is not measurable and lacks biological plausibility.
- Considering its implausibility, energy healing has attracted a surprisingly high level of research activity. Its findings are discussed in the respective chapters of each of the specific forms of energy healing.
- Generally speaking, the methodologically best trials of energy healing fail to demonstrate that it generates effects beyond placebo.
- Even though energy healing is per se harmless, it can do untold damage, not least because it significantly undermines rational thought in our societies.
As you can see, I do not entirely agree with my German friends on the issue of harm. I think energy healing is potentially dangerous and should be discouraged.
