pain
We have discussed the currently fashionable herbal remedy, ‘kratom‘, before:
Inadequate regulation of Kratom supplements put consumers at risk
News about Kratom: the herb was recently (semi-)legalized in Thailand
Kratom: a ‘herbal drug’ with the potental to do more harm than good
A quick recap:
Kratom is made of the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa, a tree endogenous to parts of Southeast Asia. It has been used traditionally for its stimulant, mood-elevating, and analgesic effects. The plant’s active constituents, mitragynine and 7-hydroxymitragynine, have been shown to modulate opioid receptors, acting as partial agonists at mu-opioid receptors and competitive antagonists at kappa- and delta-opioid receptors. Both alkaloids are G protein-biased agonists of the mu-opioid receptor and therefore, may induce less respiratory depression than classical opioid agonists. The Mitragyna alkaloids also appear to exert diverse activities at other brain receptors (including adrenergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic receptors), which may explain the complex pharmacological profile of raw kratom extracts. By the early 2000s, kratom was increasingly used in the US as a substitute for prescription and illicit opioids for managing pain and opioid withdrawal by people seeking abstinence from opioids. There are numerous assessments where people have been unable to stop using kratom and withdrawal signs and symptoms are problematic. Kratom does not appear in normal drug screens and, when taken with other substances of abuse, may not be recognized.
Now it has been reported that the family of a Florida woman who died in 2021 after ingesting kratom has been awarded more than $11m from a distributor of the herbal extract. “There is of course no amount of money that will make up for the pain and suffering that Ms Talavera’s children are enduring because of their mother’s death,” Middlebrooks wrote in court records addressing the sanction against Kratom Distro. “The law nonetheless recognizes that the defendant must pay something, however inadequate.”
The US Drug Enforcement Agency in 2016 had imposed its strictest restrictions on kratom, which is made from the leaves of an evergreen tree and is often used by people to self-treat pain, anxiety, depression, and opioid addiction as well as withdrawal. There was an intense, immediate public backlash to that approach, however, and it prompted the DEA to rescind its prohibition of kratom, which is sold in stores and online.
The US Food and Drug Administration nonetheless has warned consumers over possible safety and addiction risks associated with kratom, and it has spoken in favor of more research aimed at gaining a better understanding of “the substance and its components”.
Friends of Talavera, a resident of the Florida community of Boynton Beach, introduced her to kratom years before her death. Her family said she regarded it as a safe, natural supplement and had taken some after buying it online from the Kratom Distro when her partner and the father of her youngest child – Biagio Vultaggio – found her unconscious in the living room on 20 June 2021. The 39-year-old Talavera was face down on the ground next to an open bag of a kratom derivative marketed as a “space dust”, her family has said. Vultaggio called paramedics, and they took Talavera to a hospital where she was pronounced dead. An autopsy later listed Talavera’s cause of death as acute intoxication from mitragynine, the main kratom component. The local coroner wrote in a report that “at high concentrations, mitragynine produces opioid-like effects, such as respiratory failure”.
________________________
Kratom Disro claims that 
Product Consistency
- Our kratom powder is sourced directly from Indonesia monthly. Your order was literally on a farm in Indonesia two months ago. No old powder.
- Our kratom extracts are produced in the US by a licensed chemist and a professionally trained staff.
- We only use delicious flavors and quality ingredients.
Complete Transparency
- Every batch of products we receive is lab tested and will not ship out without meeting our meticulous quality standards.
- Current labs – We will never show you an out-of-date lab with our products.
- Guaranteed purity levels and free of all toxins.
Get It When You Want It
- Many orders shipped same day.
- USPS shipping on all orders under 6 pounds.
- Larger orders can ship USPS Priority for a small additional charge.
_________________________________
Back to the above lawsuit:
One of the attorneys for Talavera’s family, Tamara Williams, said in a statement that the judgment won by her clients “should be a wakeup call to the kratom industry”. Williams’s law firm had also recently won a $2.5m jury verdict against a kratom manufacturer in Washington state after a separate lawsuit alleging wrongful death. A colleague of Williams called on government officials to take steps “to protect other families from having to deal with unnecessary kratom overdose deaths”.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common complication of diabetes mellitus (DM) that can cause annoying symptoms. To address this condition, several treatment approaches have been proposed, including static magnetic field (SMF) therapy, which has shown promise in treating neurological conditions. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the effects of SMF therapy on symptomatic DPN and the quality of life (QoL) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial was conducted from April to October 2021. Sixty-four DPN patients (20 males, 44 females) were recruited for the study via invitation. The participants were divided into two groups: the magnet group, which used magnetic ankle bracelets (155 mT) for 12 weeks, and the sham group, which used non-magnetic ankle bracelets for the same duration. Neuropathy Symptom Score (NSS), Neuropathic Disability Score (NDS), and Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) were used to assess neuropathy symptoms and pain. In addition, the Neuropathy Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (Neuro-QoL) tool was used to measure the patients’ quality of life.
Before treatment, there were no significant differences between the magnet and sham groups in terms of the NSS scores (P = 0.50), NDS scores (P = 0.74), VAS scores (P = 0.17), and Neuro-QoL scores (P = 0.82). However, after 12 weeks of treatment, the SMF exposure group showed a significant reduction in NSS scores (P < 0.001), NDS scores (P < 0.001), VAS scores (P < 0.001), and Neuro-QoL scores (P < 0.001) compared to the baseline. The changes in the sham group, on the other hand, were not significant.
The authors concluded that according to obtained data, SMF therapy is recommended as an easy-to-use and drug-free method for reducing DPN symptoms and improving QoL in diabetic type-2 patients.
Our own study and systematic review of the effects of magnetic bracelets and similar devices suggested that the effects of such treatments are due to placebo responses. Therefore, I find the findings of this new study most surprising. Not only that, to be honest, I also find them suspect. Apart from the fact that the treatment has no biological plausibility, I have three main reasons for my skepticism.
- The authors stated that there was no distinguishable difference between the sham and SMF devices in terms of their appearance, weight, or texture, which helped to ensure that the study was double-blinded. This is nonsense, I am afraid! The verum device is magnetic and the sham device is not. It is hardly conceivable that patients who handle such devices for any length of time do not discover this simple fact and thus de-blind themselves. In turn, this means that a placebo effect can easily explain the outcomes.
- Authors who feel that their tiny study of a highly implausible therapy lends itself to concluding that their therapy ‘is recommended as an easy-to-use and drug-free method for reducing DPN symptoms and improving QoL’ can, in my view, not be taken seriously.
- Something that always makes me suspicious of clinical trials is a lack of a placebo response where one would normally expect one. In this study, the control group exhibits hardly any placebo response. Wearing a strap around your ankle that allegedly emits therapeutic radiation would result in quite a strong placebo effect, according to our own findings.
So, forgive me if I do not trust this study any further than I can throw it! And pardon me if I still think that our previous conclusion is correct: The evidence does not support the use of static magnets for pain relief, and therefore magnets cannot be recommended as an effective treatment.
In a video, Mr.Darkmoore speaks from a hospital bed and says the cause behind his visit to the emergency room stemmed from a chiropractor’s work on him. Three days ago, he had a ringing in his ear due to a long-term condition he knew as tinnitus. Thus, he decided to visit a chiropractor. “I figured $100 to a chiro, let them adjust a few things, if all else fails, I’ll go to a doctor,” explains Darkmoore.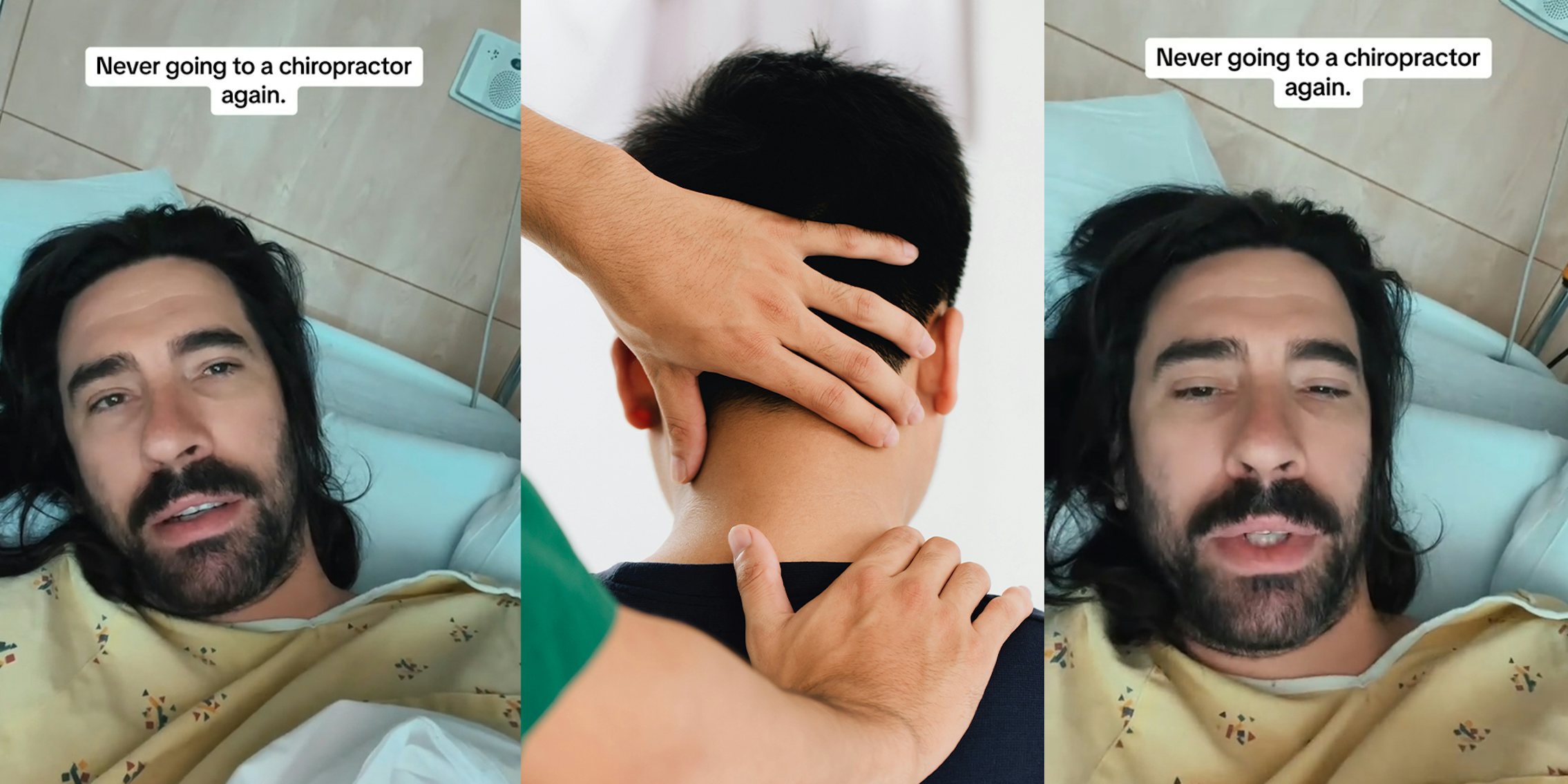
This $100 visit led to several other complications and doctor’s bills worth thousands of dollars. The day after he was treated by the chiropractor, he experienced a headache that eventually led to dizzy spells. He decided to visit the emergency room where a CT scan was ordered which showed that the chiropractor had dissected an artery in his neck.
Next, Darkmoore was put on blood thinners to avoid blood clots that could result in a stroke or worse. Darkmoore explains that he will be on two blood thinners for the next three months to prevent clotting. If the dissection heals partially, he says he will need to take aspirin every day for the rest of his life. If it doesn’t heal, he claims that he will need surgery.
Many viewers of the video claimed they have had the same “chiropractor gone wrong” experience as Darkmoore.
- “Wow. How scary. I had a similar thing happen to me. Extremely bad headache after going one time. Haven’t gone since,” one commenter wrote.
- “I’m so sorry this happened to u,” another user echoed. “My chiropractor also caused an injury which required emergency surgery & I have permanent damage. I’m glad u survived.”
Darkmore captioned his last update video, “I appreciate the thoughts and prayers. Hopefully, I’ll be okay after 3 months of recovery.”
__________________
Let’s hope that he is correct and that he will make a speedy and full recovery.
Of course, chiros will queue up to stress that important details are missing in this case report. To them, I would merely say this:
THERE IS NO GOOD EVIDENCE THAT NECK MANIPULATIONS BRING ANY BENEFIT AND QUITE A BIT OF EVIDENCE THAT THEY CAN CAUSE SERIOUS HARM.
SO, WHY NOT JUST STOP OFFERING THE PROCEDURE?
An impressive article by John Mac Ghlionn caught my attention. Allow me to quote a few passages from it:
The U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate recently reintroduced legislation to increase access to Medicare-covered services provided by chiropractors. Last year, the US chiropractic market size was worth $13.13 Billion. By the end of the decade, it will be worth over $18 billion. Each year, a whopping 35 million Americans seek chiropractic care.
But why? It’s a questionable science full of questionable characters.
Last year, a Georgia woman was left paralyzed and unable to speak after receiving a neck adjustment from a chiropractor. She’s not the first person to have had her life utterly ruined by a chiropractor, and chances are she won’t be the last. Many patients who visit chiropractors suffer severe side effects; some lose their lives…
As Dr. Steven Novella has noted, what used to be fraud is now known as holistic medicine. Dr. Edzard Ernst, a retired British-German physician and researcher, has expertly demonstrated the many ways in which chiropractic treatments are rooted not in science, but in mystical concepts…
Spinal adjustments, also known as “subluxations,” are also common. A dangerous practice that has been heavily criticized, spinal manipulations are associated with a number of adverse effects, including the risk of stroke. As Dr. Ernst has noted, the cost-effectiveness of this particular treatment “has not been demonstrated beyond reasonable doubt.”
Not content with spinal and neck manipulations, some chiropractors offer to treat other conditions — like diabetes, for example. They are not trained to treat diabetes. Other chiropractors appear to take joy in torturing infants. In August of 2018, a chiropractor made headlines for all the wrong reasons when a video emerged showing him hanging a two-week-old newborn upside down by the ankles…
Finally, as I alluded to earlier, the chiropractic community is full of fraudsters. In 2019, in the US, 15 chiropractors were charged in an insurance fraud and illegal kickback operation. More recently, in February of this year, a New York federal judge sentenced Patrick Khaziran to 30 months in prison after he pleaded guilty to being part of a widespread scheme that defrauded the NBA out of at least $5 million. In recent times, the chiropractic community has come under scrutiny for abusive care and illegal billing practices. When it comes to instances of healthcare fraud, chiropractic medicine is unrivaled.
None of this should come as a surprise. After all, the entire chiropractic community was constructed on a foundation of lies. As the aforementioned Dr. Ernst told me, we should be skeptical of what chiropractors are offering, largely because the whole practice was founded “by a deluded charlatan, who insisted that all human diseases are due to subluxations of the spine. Today, we know that chiropractic subluxations are mere figments of Palmer’s imagination. Yet, the chiropractic profession is unable to separate itself from the myth. It is easy to see why: without it, they would at best become poorly trained physiotherapists without any raison d’etre.”
… Dr. William T. Jarvis famously referred to chiropractic as “the most significant nonscientific health-care delivery system in the United States.” Comparing the chiropractic community to a cult, Dr. Jarvis wondered, somewhat incredulously, why chiropractors are licensed to practice in all 50 US states. The entire profession, he warned, “should be viewed as a societal problem, not simply as a competitor of regular health-care.”
___________________________
In my view, this is an impressive article, not least because it is refreshingly devoid of the phenomenon known as ‘false balance, e.g. a chiropractor being invited to add his self-interested views at the end of the paper claiming, for instance, “we have years of experience and cause far less harm than real doctors”.
There is widespread agreement amongst clinicians that people with non-specific low back pain (NSLBP) comprise a heterogeneous group and that their management should be individually tailored. One treatment known by its tailored design is the McKenzie method (e.g. an individualized program of exercises based on clinical clues observed during assessment) used mostly but not exclusively by physiotherapists.
A recent Cochrane review evaluated the effectiveness of the McKenzie method in people with (sub)acute non-specific low back pain. Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) investigating the effectiveness of the McKenzie method in adults with (sub)acute (less than 12 weeks) NSLBP.
Five RCTs were included with a total of 563 participants recruited from primary or tertiary care. Three trials were conducted in the USA, one in Australia, and one in Scotland. Three trials received financial support from non-commercial funders and two did not provide information on funding sources. All trials were at high risk of performance and detection bias. None of the included trials measured adverse events.
McKenzie method versus minimal intervention (educational booklet; McKenzie method as a supplement to other intervention – main comparison) There is low-certainty evidence that the McKenzie method may result in a slight reduction in pain in the short term (MD -7.3, 95% CI -12.0 to -2.56; 2 trials, 377 participants) but not in the intermediate term (MD -5.0, 95% CI -14.3 to 4.3; 1 trial, 180 participants). There is low-certainty evidence that the McKenzie method may not reduce disability in the short term (MD -2.5, 95% CI -7.5 to 2.0; 2 trials, 328 participants) nor in the intermediate term (MD -0.9, 95% CI -7.3 to 5.6; 1 trial, 180 participants).
McKenzie method versus manual therapy There is low-certainty evidence that the McKenzie method may not reduce pain in the short term (MD -8.7, 95% CI -27.4 to 10.0; 3 trials, 298 participants) and may result in a slight increase in pain in the intermediate term (MD 7.0, 95% CI 0.7 to 13.3; 1 trial, 235 participants). There is low-certainty evidence that the McKenzie method may not reduce disability in the short term (MD -5.0, 95% CI -15.0 to 5.0; 3 trials, 298 participants) nor in the intermediate term (MD 4.3, 95% CI -0.7 to 9.3; 1 trial, 235 participants).
McKenzie method versus other interventions (massage and advice) There is very low-certainty evidence that the McKenzie method may not reduce disability in the short term (MD 4.0, 95% CI -15.4 to 23.4; 1 trial, 30 participants) nor in the intermediate term (MD 10.0, 95% CI -8.9 to 28.9; 1 trial, 30 participants).
The authors concluded that, based on low- to very low-certainty evidence, the treatment effects for pain and disability found in our review were not clinically important. Thus, we can conclude that the McKenzie method is not an effective treatment for (sub)acute NSLBP.
The hallmark of the McKenzie method for back pain involves the identification and classification of nonspecific spinal pain into homogenous subgroups. These subgroups are based on the similar responses of a patient’s symptoms when subjected to mechanical forces. The subgroups include postural syndrome, dysfunction syndrome, derangement syndrome, or “other,” with treatment plans directed to each subgroup. The McKenzie method emphasizes the centralization phenomenon in the assessment and treatment of spinal pain, in which pain originating from the spine refers distally, and through targeted repetitive movements the pain migrates back toward the spine. The clinician will then use the information obtained from this assessment to prescribe specific exercises and advise on which postures to adopt or avoid. Through an individualized treatment program, the patient will perform specific exercises at home approximately ten times per day, as opposed to 1 or 2 physical therapy visits per week. According to the McKenzie method, if there is no restoration of normal function, tissue healing will not occur, and the problem will persist.
Classification:
The postural syndrome is pain caused by mechanical deformation of soft tissue or vasculature arising from prolonged postural stresses. These may affect the joint surfaces, muscles, or tendons, and can occur in sitting, standing, or lying. Pain may be reproducible when such individuals maintain positions or postures for sustained periods. Repeated movements should not affect symptoms, and relief of pain typically occurs immediately following the correction of abnormal posture.
The dysfunction syndrome is pain caused by the mechanical deformation of structurally impaired soft tissue; this may be due to traumatic, inflammatory, or degenerative processes, causing tissue contraction, scarring, adhesion, or adaptive shortening. The hallmark is a loss of movement and pain at the end range of motion. Dysfunction has subsyndromes based upon the end-range direction that elicits this pain: flexion, extension, side-glide, multidirectional, adherent nerve root, and nerve root entrapment subsyndromes. Successful treatment focuses on patient education and mobilization exercises that focus on the direction of the dysfunction/direction of pain. The goal is on tissue remodeling which can be a prolonged process.
The derangement syndrome is the most commonly encountered pain syndrome, reported in one study to have a prevalence as high as 78% of patients classified by the McKenzie method. It is caused by an internal dislocation of articular tissue, causing a disturbance in the normal position of affected joint surfaces, deforming the capsule, and periarticular supportive ligaments. This derangement will both generate pain and obstruct movement in the direction of the displacement. There are seven different subsyndromes which are classified by the location of pain and the presence, or absence, of deformities. Pain is typically elicited by provocative assessment movements, such as flexion or extension of the spine. The centralization and peripheralization of symptoms can only occur in the derangement syndrome. Thus the treatment for derangement syndrome focuses on repeated movement in a single direction that causes a gradual reduction in pain. Studies have shown approximately anywhere between 58% to 91% prevalence of centralization of lower back pain. Studies have also shown that between 67% to 85% of centralizers displayed the directional preference for a spinal extension. This preference may partially explain why the McKenzie method has become synonymous with spinal extension exercises. However, care must be taken to accurately diagnose the direction of pain, as one randomized controlled study has shown that giving the ‘wrong’ direction of exercises can actually lead to poorer outcomes.
Other or Nonmechanical syndrome refers to any symptom that does not fit in with the other mechanical syndromes, but exhibits signs and symptoms of other known pathology; Some of these examples include spinal stenosis, sacroiliac disorders, hip disorders, zygapophyseal disorders, post-surgical complications, low back pain secondary to pregnancy, spondylolysis, and spondylolisthesis.
CONCLUSION:
“Internationally researched” and found to be ineffective!
This study allegedly evaluated the efficacy of osteopathic manipulative therapy (OMT) compared to that of the Kaltenborn-Evjenth Orthopedic Manipulative Therapy (KEOMT) for patients with chronic LBP.
It included 68 participants of both genders, aged 30 to 60, with chronic LBP. Participants were randomly assigned to one of two parallel groups, each with 34 members. The OMT group received, as a direct technique, a high-velocity/low-amplitude (HVLA) impulse, and as indirect techniques, strain counterstrain (SCS), myofascial release (MFR), and visceral mobilization therapy (VMT). The KEOMT group received lumbar segmental traction and lumbar segmental mobilization-flexion and gliding therapy grade 3. The participants in both groups received 10 treatments, two per week for five weeks. The primary outcome was pain severity, using a numeric pain rating scale (NPRS). The secondary outcome was the measurement of functional disability, using the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI).
The OMT and KEOMT both decreased pain and disability; however, the changes on the NPRS and ODI postintervention were statistically greater for the OMT group compared to the KEOMT group (P < .05).
The authors concluded that the OMT was better at reducing pain and improving quality of life. It reduced functional disability more than KEOMT in patients with chronic LBP.
The Kaltenborn-Evjenth Orthopedic Manipulative Therapy (KEOMT) concept is a treatment and training system based upon a comprehensive biomechanical evaluation of the arthro-neuro-muscular system and an individual’s functional abilities. This system of diagnosis and patient management applies to both patients with acute, subacute and chronic conditions of the spine and extremities and to athletes seeking to improve performance. It offers a reliable and practical approach that focuses on optimal physical health and function.
Has the KEOMT concept been tested and shown to be effective for LBP?
No!
So, what we have here is an equivalence trial of two manual techniques. As such it is FAR too small to yield a meaningful result. If the findings were meaningful, would they show that OMT is effective?
No!
As we have no proof that KEOMT does not impede recovery from LBP, the result could merely be due to the fact that OMT does not influence the natural history of LBP, while KEOMT has a detrimental effect.
Last question: which journal publishes such rubbish?
Ahh, it’s the remarkable Alternative therapies in health and medicine. That explains a lot!
This trial investigated the effect of osteopathic visceral manipulation (OVM) on disability and pain intensity in individuals with functional constipation and chronic nonspecific low back pain. It was designed as a randomized controlled trial with a blinded assessor. Seventy-six volunteers with functional constipation and chronic nonspecific low back pain were randomized to two groups: OVM and sham OVM. The primary clinical outcome was pain intensity measured using a numeric rating scale (NRS) and disability measured using the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI). The secondary outcomes were electromyographic signals measured during the flexion-extension cycle, the finger-to-floor distance during complete flexion of the trunk, and the Fear-Avoidance Beliefs Questionnaire (FABQ). All outcomes were determined after six weeks of treatment as well as three months after randomization.
The OVM group reported a reduction in pain intensity after six weeks of treatment and at the three-month evaluation (p < .0002) and the sham group reported a reduction in pain intensity after three-month evaluation (p < .007). For the ODI was also found in the OVM group six weeks after the end of treatment (treatment effect = -6.59, 95% CI: -12.01 to -1.17, p = .01) and at the three-month evaluation (treatment effect = -6.02, 95% CI: -11.55 to -0.49, p = .03). Significant differences were also found for paravertebral muscle activity during the dynamic phases (flexion and extension) six-week evaluations.
The authors concluded that the OVM group demonstrated a reduction in pain intensity and improvement in disability after six-weeks and three-month follow-up while the sham group reduction in pain three-month follow-up.
I have no access to the full paper (if someone can send me the paper, I would update my post accordingly), but from reading the abstract, it seems the reported findings are based on within-group changes. The whole point of having a control group is to compare verum and control. The other point of importance is that it would have been crucial to verify whether patients were able to tell the verum from the sham intervention. If patients were able to tell, they would no longer be blinded and the placebo effect would have not been accounted for. A third point of relevance might be that the study seems tiny and far too small for drawing general conclusions about the value of OVM.
_________________________
I have now seen the protocol of the paper – thanks for making it available – and might add the following points to the discussion:
- The sham treatment consisted of “light touches over the different parts of the abdomen, without any deep mobilization or movement. The osteopath applied her hands over the same points with the
same duration as in OVM to give the patient the perception of being treated.” It is likely that patients in the control group could have guessed that they were sham-treated. - The stats issue cannot be resolved on the basis of just the protocol.
- “To assess patients’ blinding to treatment allocation, patients are asked post treatment (six weeks after
the start of treatment) to report which study treatment they think that they received (OVM/SOVM). The effect of their reports on outcome will be examined in explorative analysis.” As I have no
access to the results, I still do not know whether blinding was successful.
Lumbosacral Radicular Syndrome (LSRS) is a condition characterized by pain radiating in one or more dermatomes (Radicular Pain) and/or the presence of neurological impairments (Radiculopathy). So far, different reviews have investigated the effect of HVLA (high-velocity low-amplitude) spinal manipulations in LSRS. However, these studies included ‘mixed’ population samples (LBP patients with or without LSRS) and treatments other than HVLA spinal manipulations (e.g., mobilisation, soft tissue treatment, etc.). Hence, the efficacy of HVLAT in LSRS is yet to be fully understood.
This review investigated the effect and safety of HVLATs on pain, levels of disability, and health-related quality of life in LSRS, as well as any possible adverse events.
Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) published in English in the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE (PubMed), EMBASE, PEDro, and Web of Science were identified. RCTs on an adult population (18-65 years) with LSRS that compared HVLATs with other non-surgical treatments, sham spinal manipulation, or no intervention were considered. Two authors selected the studies, extracted the data, and assessed the methodological quality through the ‘Risk of Bias (RoB) Tool 2.0’ and the certainty of the evidence through the ‘GRADE tool’. A meta-analysis was performed to quantify the effect of HVLA on pain levels.
A total of 308 records were retrieved from the search strings. Only two studies met the inclusion criteria. Both studies were at high RoB. Two meta-analyses were performed for low back and leg pain levels. HVLA seemed to reduce the levels of low back (MD = -1.48; 95% CI = -2.45, -0.50) and lower limb (MD = -2.36; 95% CI = -3.28, -1.44) pain compared to other conservative treatments, at three months after treatment. However, high heterogeneity was found (I² = 0.0%, p = 0.735). Besides, their certainty of the evidence was ‘very low’. No adverse events were reported.
The authors stated that they cannot conclude whether HVLA spinal manipulations can be helpful for the treatment of LSRS or not. Future high-quality RCTs are needed to establish the actual effect of HVLA manipulation in this disease with adequate sample size and LSRS definition.
Chiropractors earn their living by applying HVLA thrusts to patients suffering from LSRS. One would therefore have assumed that the question of efficacy has been extensively researched and conclusively answered. It seems that one would have assumed wrongly!
Now that this is (yet again) in the open, I wonder whether chiropractors will, in the future, tell their patients while obtaining informed consent: “I plan to give you a treatment for which sound evidence is not available; it can also cause harm; and, of course, it will cost you – I hope you don’t mind.”
An explanatory sequential mixed methods study with three separate phases was conducted in Danish patients with lumbar radiculopathy receiving a standardized chiropractic care package (SCCP). Lumbar radiculopathy is pain and other neurological symptoms caused by the pinching of nerve roots where they leave your spinal cord in the lumbar region. 
Phase one of the study was a quantitative analysis based on a survey in a prospective cohort of patients with lumbar radiculopathy in an SCCP from 2018 to 2020. Patients rated their satisfaction with the examination, information, treatment effect, and overall management of their problem on a 0–10 scale. In phase two, six semi-structured interviews conducted in 2021 were used to gain further explanatory insights into the findings from phase one. Data were analyzed using systematic text condensation. In phase three, the quantitative and qualitative data were merged in a narrative joint display to obtain a deeper understanding of the overall results.
Here I am only interested in the patients’ perception of the treatment effect. Of 303 eligible patients, 238 responded to the survey. Of these, 50% were very satisfied with the treatment effect.
The authors stated that patients in their study expected a rapid and persistent decrease in symptoms, which, unfortunately, does not match the prognosis of lumbar radiculopathy. Although the prognosis is considered good, the improvement happens gradually and often with fluctuating pain patterns, and it is not unusual to have milder symptoms for three months or longer.
So, only half of the patients who had chosen to consult chiropractors for their lumbar radiculopathy were very satisfied with the treatment results. In most patients, the symptoms decreased only gradually often with fluctuating pain patterns, and the authors comment that symptoms frequently last for three months or longer with a SCCP.
Impressive?
Might I point out that what is being described here looks to me very much like the natural history of lumbar radiculopathy? About 90% of patients with back pain caused by disc herniation see improvements within three months without therapy. Are the authors aware that their observational study is in accordance with the notion that the SCCP does nothing or very little to help patients suffering from lumbar radiculopathy?
Low back pain is the leading cause of years lived with disability globally, but most interventions have only short-lasting, small to moderate effects. Cognitive functional therapy (CFT) is an individualized approach that targets unhelpful pain-related cognitions, emotions, and behaviors that contribute to pain and disability. Movement sensor biofeedback might enhance treatment effects.
This study aimed to compare the effectiveness and economic efficiency of CFT, delivered with or without movement sensor biofeedback, with usual care for patients with chronic, disabling low back pain.
RESTORE was a randomized, three-arm, parallel-group, phase 3 trial, done in 20 primary care physiotherapy clinics in Australia. The researchers recruited adults (aged ≥18 years) with low back pain lasting more than 3 months with at least moderate pain-related physical activity limitation. Exclusion criteria were serious spinal pathology (eg, fracture, infection, or cancer), any medical condition that prevented being physically active, being pregnant or having given birth within the previous 3 months, inadequate English literacy for the study’s questionnaires and instructions, a skin allergy to hypoallergenic tape adhesives, surgery scheduled within 3 months, or an unwillingness to travel to trial sites. Participants were randomly assigned (1:1:1) via a centralized adaptive schedule to
- usual care,
- CFT only,
- CFT plus biofeedback.
The primary clinical outcome was activity limitation at 13 weeks, self-reported by participants using the 24-point Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire. The primary economic outcome was quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). Participants in both interventions received up to seven treatment sessions over 12 weeks plus a booster session at 26 weeks. Physiotherapists and patients were not masked.
Between Oct 23, 2018, and Aug 3, 2020, the researchers assessed 1011 patients for eligibility. After excluding 519 (51·3%) ineligible patients, they randomly assigned 492 (48·7%) participants; 164 (33%) to CFT only, 163 (33%) to CFT plus biofeedback, and 165 (34%) to usual care. Both interventions were more effective than usual care (CFT only mean difference –4·6 [95% CI –5·9 to –3·4] and CFT plus biofeedback mean difference –4·6 [–5·8 to –3·3]) for activity limitation at 13 weeks (primary endpoint). Effect sizes were similar at 52 weeks. Both interventions were also more effective than usual care for QALYs, and much less costly in terms of societal costs (direct and indirect costs and productivity losses; –AU$5276 [–10 529 to –24) and –8211 (–12 923 to –3500).
The authors concluded that CFT can produce large and sustained improvements for people with chronic disabling low back pain at considerably lower societal cost than that of usual care.
This is a well-designed and well-reported study. It shows that CFT is better than usual care. The effect sizes are not huge and seem similar to many other treatments for chronic LBP, including the numerous so-called alternative medicine (SCAM) options that are available.
Faced with a situation where we have virtually dozens of therapies of similar effectiveness, what should we recommend to patients? I think this question is best and most ethically answered by accounting for two other important determinants of usefulness:
- risk
- cost.
CFT is both low in risk and cost. So is therapeutic exercise. We would therefore need a direct comparison of the two to decide which is the optimal approach.
Until we have such a study, patients might just opt for one or both of them. What seems clear, meanwhile, is this: SCAM does not offer the best solution to chronic LBP. In particular, chiropractic, osteopathy, or acupuncture – which are neither low-cost nor risk-free – are, contrary to what some try so very hard to convince us of, sensible options.

